|
| LEADER OF ELECTROLYSIS TECHNOLOGY |
Approximate 100% Air Disinfection and Sterilization Effect
- Fanslly-800 Sterilization Test Report
- Approximate 100% Air Disinfection and Sterilization Effect
International renowned testing organization INTERTEK testing Fanslly-800 Hypochlorous Acid Liquid sprayed by SuperAqua Dry Mist Sprayer, it can reduce bacteria by 99.44% and fungi by 96.55% in just 1 minute. The effect is so amazing, see. - SuperAqua versus Epidemic Prevention
- Super Aqua Products for Disinfection
Latest News
-
Anti-Epidemic Fanslly Donate Fans...
The epidemic alert has lowered down to level 2 would cause increase demand on sterlizer especially in public venue and household, ...
SGS: Skin-friendly Hypochlorous Ac...
There are so many hypochlorous acid products in the market, how to choose? One is safe to body, and the other is...
Sanjay Dutt, Super Aqua's user
Sanjay Dutt, the Indian award winning movie star, met SuperAqua's epidemic prevention in year 2020. Noted on Fanslly-800...

Alkaline Ionized Water
Alkaline ionized water is alkaline water produced by an alkaline ionized water device (a.k.a. alkaline ionized water generator) from raw water directly and also electrolyzed reduce water known to the public. Alkaline ionized water is scientifically defined as the “weak-base low-voltage micro-molecule drinking water” (or the “reductive water” in Japan).

Super Aqua new-generation sterilization technique
The 100% hypochlorous-acid liquid is the core technique first developed by Mr.Tatsuo Okazaki, President of Okazaki Manufacture Company (OMCO) and a revolutionary product changing the history of sterilization and contributing to the Earth as well as human and environmental health.

OEM/ODM equipment
Superb background for electrolysis technologies and 1,000 patents in 40 years
Super Aqua follows a customer’s expectations or demands to design customized series of products: Household electrolyzers series (with filters included), commercial electrolyzers series, electrolyzed hypochlorous-acid liquid generator series, and ancillary equipment series.
新世代殺菌技術
Applications of Super Aqua products
Applications of Super Aqua products in different industries
Beverage and food industry:
Beverage factory; milk plant; bottled water factory; juice factory; meat packer; vegetable processing plant; fruit processing plant; noodle factory; fresh food factory; catering
Fishing industry; fish processing industry; seafood & livestock industry; food processing industry
Food & beverage factory:
- Cleaning of food materials
-
Cleaning water for buildings
Floor; wall; ceiling; toilet; handrail; door knob; others
- Finger cleaning and sterilization
- Strategy for airborne microbes and falling bacteria at a production line (based on aerosol products)
- Floor cleaning
- Cleaning of manufacturing equipment, facilities, heat sterilizers, fillers and others
- Strategy for bacillus
- Strategy for bacteria and mold adhering to ceilings and floors
- Cleaning of conveyer belts (particularly entry, inner side, and roller)
- Cleaning of mixers, raw material bins, water tanks and others
- Sterilization and deodorization of wastes
- Cleaning of filler containers and lids
- Cleaning of hoses, warehouses and containers
- Cleaning inside tubes before filling of other products
- Deodorization
Pool & SPA:
- Sterilization of pool water (avoiding pink eyes)
- Health management of SPA (high-temperature (42°C) sterilization for customers)
- Sterilization of bath towels and bedding
- Sterilization and deodorization of bathrooms and toilets
- Others


Five-star hotel & business club:
- Health management of pools and SPA pools
- Sterilization of bath towels, bedclothes and bedding
- Health management of restaurants, Japanese cuisine restaurants, tableware and kitchens
- Health management of guest rooms, bathrooms and toilets (for deodorization and removal of stale odor)
- Health management of public space and environment

Restaurant, hypermarket and supermarket chain:
- Sterilization of food materials (purchased fresh vegetables, fruits, etc.)
- Health management of kitchen counters for raw food processing
- Sterilization of knifes, apparatus, equipment, tanks and freezers
- Sterilization of tableware, tables and chairs
- Hand washing of employees (with sterilizing water replacing alcohol)
- Health management of space and environment

Snack bar, catering and fresh food factory:
- Sterilization of food materials (purchased fresh vegetables, fruits, etc.)
- Sterilization of knifes, apparatus, equipment, tanks and freezers
- Sterilization of tableware, tables and chairs
- Hand washing of employees (with sterilizing water replacing alcohol)
- Health management of space and environment

MRT, public transit and station:
- Sterilization of transportation, vehicles and seats
- Health management of space and environment

School and kindergarten:
- Regular health management of classrooms, desks, chairs, equipment and instruments
- Health management of pools and toilets
- Sterilization of knifes, apparatus, equipment, tanks and freezers in kitchens
- Sterilization of tableware
- Hand washing of students and teachers
- Health management of space and environment

Pet or pet shop:
- Bathing and deodorization of pets (dermatosis or wound healing)
- Sterilization and deodorization of feeding areas
- Sterilization of feeders, equipment and tanks
- Hand washing of employees
- Health management of space and environment

Hospital & clinic:
- Cleaning and sterilization of endoscope, medical apparatus, etc.
- Cleaning and sterilization of equipment, instruments and consulting rooms
- Sterilization of hospital beds, bedclothes, bedding, etc.
- Sterilization of wards, bathrooms, toilets, floors, etc.
- Sprayer-based sterilization inside a hospital; strategy for nosocomial infections
- Wound treatments of patients suffering diabetes or pressure ulcer (by doctors)
- Others (hand washing, restaurant, kitchen, laundry, surroundings, etc.)

Dental clinic:
- Sterilization of dental equipment
- Root canal therapy (with sterilizing water replacing sodium hypochlorite)
- Cleaning and sterilization of equipment, instruments and consulting rooms
- Sprayer-based sterilization inside a clinic; strategy for nosocomial infections
Troop:
- Sterilization and health management of ships (removal of stale odor)
- Sterilization of food materials, kitchens, knifes, apparatus, equipment, tanks, freezers and tableware
- Sterilization of sleeping quarters, bedclothes, bedding, etc.
- Health management of bathrooms and toilets

Nursing home & health village:
- Health management of equipment, instruments and consulting rooms
- Sterilization of beds, bedclothes, bedding, etc.
- Sterilization of bathrooms, toilets and floors
- Sprayer-based sterilization; strategy for infections
- Strategy of doctors for pressure ulcer


Environment protection (e.g., tap water):
-
Upgrade of tap water treatment:
- Sterilization in a water treatment plant
- Water outlet at the back end (sodium hypochlorite)
- Sterilization of liquid waste and sewage
- Dyeing and finishing plant (comparisons of sterilization effects)

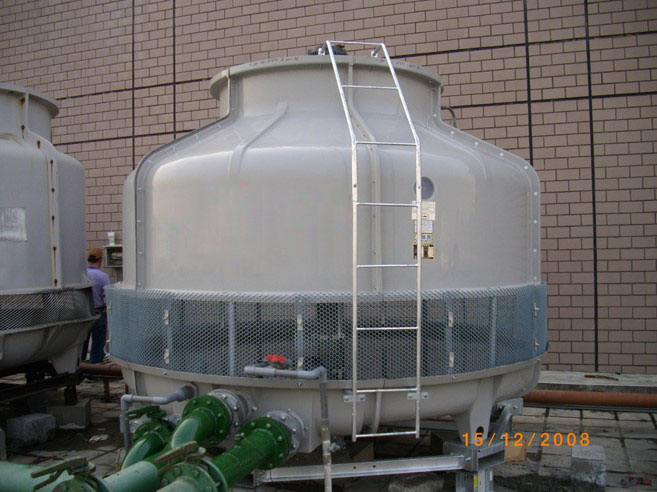
Cooling tower system:
-
Characteristics of Super Aqua sterilizing water applied to a cooling tower system:
- Higher temperature for better sterilization effect
- Safety (food grade)
- No disadvantages in the past
- Please refer to the solutions of Super Aqua for bio-membrane with bacteria, incrustation and algae.

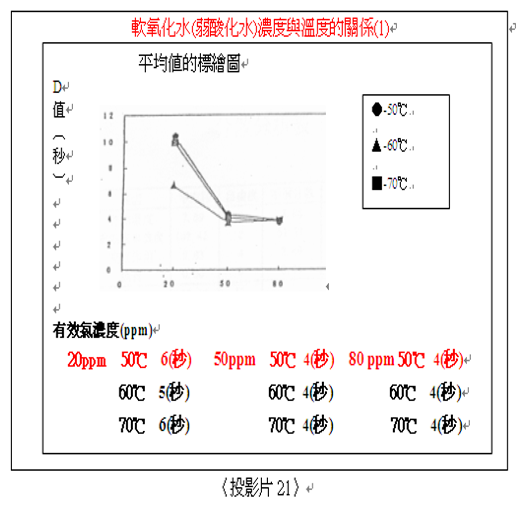
Sterilization effect of temperature and hypochlorous acid for mould spores of B. circulans:
(Source: Japan Soft Drink Journal, 1998) Information:
< Higher temperature for better sterilization effect >
Government notice or technology transfer
(1) Technology Transfer from the Food Industry Research and Development Institute, Taiwan :
The optimum cleaning and sterilization technique for fresh oysters and fillets
Cooperation model: technology transfer
Background introduction: ( Note; Chinese Version only)
As the core elements of a seafood factory, both sanitary safety and superb product quality enhance a company’s competitive advantages compared with the same trades. In this regard, the introduction of modernized health control equipment for promotion of health management technologies improves an enterprise’s competitive advantages.
The weak-acid sterilizing water with the sterilization effect 50 times as much as sodium hypochlorite for instant sterilization is reduced to ordinary water after sterilization and characteristic of the pH value between 4.0 and 6.5. Based on hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as the major ingredient for sterilization in sodium hypochlorite, the technique of acidic sterilizing water is to produce stable and qualified acidic sterilizing water from the sterilizing water generator in which the concentration is configured. The acidic sterilizing water, which is effective in sterilization and safer than sodium hypochlorite and features less adverse effect (corrosive effect) on food materials (equipment), practicability and low costs, has been widely used in various industries or institutes for sterilization such as food industry, hospital, stock farming, hospitality industry and public places in Japan, Korea, Europe and America.
The high-concentration electrolyzed ozone water generator is a high-tech product developed in recent years. Based on PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) electrolysis, the ozone generator, which electrolyzes pure water for production of ozone, is able to manufacture ozone water directly with proprietary filtering and air-water mixing techniques integrated. Featuring fast oxidation and decomposition, the high-concentration electrolyzed ozone water is effective in deodorization and sterilization of foods and utensils, oxidation and decomposition of residual pesticides on vegetables and fruits, and removal and deodorization of chlorine remained in water for various commercial applications such as vegetable & fruit processing center, food factory, seafood processing center, laundry, pool, cooling tower, stock farming and aquaculture.
To obey standards of food & sanitation laws for microbes, the optimized method of cleaning and sterilizing oysters and fillets uses both weak-acid sterilizing water and high-concentration electrolyzed ozone water.

Technologies to be transferred:
- Evaluations of sterilization effects of newly-developed weak-acid sterilizing water and high-concentration electrolyzed water on microbes according to consumption, pH value, stability, concentration, temperature and time
- Evaluations of sterilization effects of newly-developed weak-acid sterilizing water and high-concentration electrolyzed water on fresh fillets according to consumption, pH value, stability, concentration, temperature and time
Contact window:
Please refer to Super Aqua
Technology Transfer Survey
| Title | The optimized method to clean and sterilize seafood including fresh oysters and fillets |
|---|---|
| Item No. | |
| Description | Control of microbes and extension of shelf lives by cleaning and sterilization techniques |
| Applicable industry | Fishery and other food industries |
| Applicable products | Fresh oysters and fillets |
| Technical specifications | Evaluations of sterilization effects of weak-acid sterilizing water and high-concentration electrolyzed ozone water on fresh fillets according to concentration, temperature, pH value and time consumption |
| Features | Acidic sterilizing water with neither trichloromethane nor toxic gases such as high-concentration electrolyzed ozone and nitric oxide (NOx) |
| Granted patent | |
| Benefit (output value) |
Promotion of sanitary safety and product quality |
| Recommendation for technology-transfer applicants | Cleaning and sterilization of equipment and workplaces |
| Contact window for techniques | |
| Contact window for technology transfer | |
| Costs and methods for technology transfer |
For more detailed information, please refer to Super Aqua:
(2) Notice for employment of hypochlorous acid liquids issued by the Ministry of Health and Welfare,R.O.C.( Taiwan ):
Appendix1. The substances which used to disinfect food-contact surfaces shall apply to:
| NO | CAS Reg. | No. | Substance Use limitation* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64-19-7 | Acetic acid | 686 ppm |
| 2 | 98-55-5 | Alpha-terpineol | None (Note 2) |
| 3 | 12125-02-9 | Ammonium chloride | 48 ppm |
| 4 | 10043-52-4 | Calcium chloride | 17 ppm |
| 5 | 7778-54-3 | Calcium hypochlorite | 200 ppm as total available chlorine (Note 2) |
| 6 | 1592-23-0 | Calcium stearate | None |
| 7 | 3347-48-5 | Decanoic acid | Dairy processing equipment: 90 ppm Other food-contact surfaces: 234 ppm |
| 8 | 7173-51-5 | Didecyldimethylammonium chloride | Active quaternary compound: 200 ppm (Note 2) |
| 9 | 139-33-3 | Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate | 1400 ppm |
| 10 | 27176-87-0 | Dodecyl-benzenesulfonic acid | Dairy processing equipment: 5.5 ppm Other food-contact surfaces: 400 ppm |
| 11 | 64-17-5 | Ethanol | None |
| 12 | 111-76-2 | Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether | None (Note 2) |
| 13 | 7790-92-3 |
Hypochlorous acid
|
200 ppm as total available chlorine |
| 14 | 10034-85-2 | Hydriodic acid | 25 ppm of titratable iodine |
| 15 | 7722-84-1 | Hydrogen peroxide | Dairy processing equipment: 465 ppm Other food-contact surfaces: 1100 ppm |
| 16 | 7553-56-2 | Iodine | 25 ppm of titratable iodine |
| 17 | 13840-33-0 | Lithium hypochlorite | 200 ppm as total available chlorine and 30 ppm lithium (Note 2) |
| 18 | 50-21-5 | Lactic acid | Dairy processing equipment: 138 ppm Other food-contact surfaces: None |
| 19 | 1309-48-4 | Magnesium oxide | None |
| 20 | 7558-80-7 | Monosodium phosphate | 350 ppm |
| 21 | 26896-20-8 | Neo-decanoic acid | 174 ppm (Note 2) |
| 22 | 7697-37-2 | Nitric acid | 1000 ppm |
| 23 | 112-05-0 | Nonanoic acid | 90 ppm |
| 24 | 7378-99-6 | N,N-dimethyloctanamine | 113 ppm |
| 25 | 124-07-2 | Octanoic acid | Dairy processing equipment: 176 ppm Other food-contact surfaces: 234 ppm |
| 26 | 3944-72-7 | 1-Octanesulfonic acid | 172 ppm (Note 2) |
| 27 | 28805-58-5 | Octenyl succinic acid | 156 ppm |
| 28 | 90-43-7 | ortho-Phenylphenol | 400 ppm (Note 2) |
| 29 | None | Oxychloro species (predominantly chlorite, chlorate and chlorine dioxide in an equilibrium mixture) generated either (i) by directly metering a concentrated chlorine dioxide solution prepared just prior to use, into potable water, or (ii) by acidification of an aqueous alkaline solution of oxychloro species (predominately chlorite and chlorate) followed by dilution with potable water | 200 ppm as total available chlorine |
| 30 | None | Oxychloro species (including chlorine dioxide) generated by acidification of an aqueous solution of sodium chlorite. | 200 ppm as total available chlorine |
| 31 | 79-21-0 | Peroxyacetic acid | 315 ppm |
| 32 | 33734-57-5 | Peroxyoctanoic acid | 122 ppm |
| 33 | 2809-21-4 | 1-hydroxyethylidene-1 1- diphosphonic acid (HEDP) | 34 ppm |
| 34 | 7664-38-2 | Phosphoric acid | None |
| 35 | 7758-02-3 | Potassium bromide | Dairy processing equipment: 46 ppm total available halogen Other food-contact surfaces: 200 ppm total available halogen |
| 36 | 7681-11-0 | Potassium iodide | 25 ppm of titrateble iodine |
| 37 | 7778-66-7 | Potassium hypochlorite | 200 ppm as total available chlorine (Note 2) |
| 38 | 79-09-4 | Propionic acid | 297 ppm |
| 39 | 499-83-2 | 2,6-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid | 1.2 ppm |
| 40 | 8001–54–5 | (Quaternary ammonium compounds, including cetylpyridinium chloride) 1.alkyl (C12-C18) benzyldimethyl, chlorides |
the end-use concentration of all quaternary chemicals in the solution is not to exceed 200 ppm of active quaternary compound |
| 41 | 68424–85–1 | 2.n-alkyl (C12-18) dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride | the end-use concentration of all quaternary chemicals in solution is not to exceed 400 ppm of active quaternary compound |
| 42 | 85409–23–0 | 3.n-alkyl (C12-14) dimethyl ethylbenzyl ammonium chloride, average molecular weight (in amu), 377to 384. | the end-use concentration of all quaternary chemicals in solution is not to exceed 400 ppm of active quaternary compound |
| 43 | None | 4.n-alkyl (C12-18) dimethyl ethylbenzyl ammonium chloride, average molecular weight (in amu) 384. | the end-use concentration of all quaternary chemicals in the solution is not to exceed 400 ppm of active quaternary compound |
| 44 | None | 5.di-n-Alkyl(C8-10) dimethyl ammonium chloride, average molecular weight (in amu) 332 to 361. | the end-use concentration of these specific in quaternary ammonium compounds is not to exceed 240 ppm of active quaternary ammonium compound; the end-use concentration of all quaternary chemicals in the solution is not to exceed 400 ppm of active quaternary compound |
| 45 | 148788–55–0 /148812–654–1 |
6.didecyl dimethyl ammonium carbonate /didecyl dimethyl ammonium bicarbonate |
the end-use concentration of these specific ammonium compounds is not to exceed 240 ppm of active quaternary ammonium compound |
| 46 | 5324-84-5 | Sodium 1-octanesulfonate | 312 ppm (Note 2) |
| 47 | 7647-15-6 | Sodium bromide | 200 ppm total available halogen (Note 2) |
| 48 | 527-07-1 | Sodium gluconate | 760 ppm |
| 49 | 7681-52-9 1310-73-2 |
Sodium hypochlorite | 200 ppm as total available chlorine |
| 50 | 7681-82-5 | Sodium iodide | 25 ppm of titratable iodine (Note 2) |
| 51 | 7775-19-1 | Sodium metaborate | None (Note 2) |
| 52 | 68309-27-3 | Sulfonated tall oil fatty acid | 66 ppm (Note 2) |
| 53 | 7664-93-9 | Sulfuric acid | 228 ppm (Note 2) |
| 54 | 64-02-8 | Tetrasodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate | None |
*”Limitations” means the end-use concentration maximum limits, when ready for use.
- Note 1. In composite formulation's product, each single component's concentration limits shall apply this table.
- Note 2. Not apply to dairy processing equipment.
- Note 3. Used to the cleanser substances in this table, should adequate draining or dried volatile to avoid detergent residue on food contact surfaces.
Appendix2. The substances which used to disinfect food shall apply to:
| NO | CAS Reg. No. | Substance | Residue Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | Acidified sodium chlorite solutions (ASC) (Note 2) |
Not more than 1 ppm as total available chlorine. |
| 2 | 10049-04-4 | Chlorine dioxide | Not more than 1 ppm as total available chlorine. |
| 3 | 7790-92-3 | Hypochlorous acid | Not more than 1 ppm as total available chlorine. |
| 4 | 7681-52-9 | Sodium hypochlorite | Not more than 1 ppm as total available chlorine. |
- Note 1. After used for the compounds listed in the table, shall be followed by a potable water rinse or by blanching or cooking, the final food contains no more than the limitations specified in the Table.
- Note 2. Acidified sodium chlorite solutions (ASC): The substance is produced by mixing an aqueous solution of sodium chlorite (CAS Reg. No. 7758-19-2) with any generally recognized as safe (GRAS) acid; achieve a pH of 2.3 to 2.9.
Super Aqua 技術資料
Superaquaに関する基本資料
Technical Data on Super Aqua HCLOTechnology
| Japanese | English |
|---|---|
| 1. ベーシックトレーニングソフト酸化水編 A. ソフト酸化水の概念 1.A.1 酸化水の発展史 1.A.2 ソフト酸化水とは? 1.A.3 ソフト酸化水のpH5の重要性 1.A.4 ソフト酸化水の生成原理 1.A.5 電解添加液の塩酸の意味 1.A.6 殺菌のメカニズム 1.A.7 ソフト酸化水の殺菌メカニズム B. ソフト酸化水殺菌効果試験 1.B.1 試験内容と方式の説明 1.B.2 試験菌の種類 1.B.3 試験結果 1.B.4 まとめ C. 有機物存在化での殺菌効果試験 1.C.1 試験内容と方式の説明 1.C.2 試験菌の種類 1.C.3 試験結果 1.C.4 まとめ D. ソフト酸化水保存性試験 1.D.1 試験内容と方式の説明 1.D.2 まとめ E. ソフト酸化水動物安全性試験 1.E.1 試験項目 1.E.2 試験内容の説明 1.E.3 まとめ F. ソフト酸化水動物安全性試験結果報告 |
1. Basic Training about Super Aqua A. Concepts about Super Aqua 1.A.1 The Development of Super Aqua 1.A.2 What is Super Aqua? 1.A.3 The Importance of Super Aqua whose pH value is pH5 1.A.4 The Producing Principles of Super Aqua 1.A.5 What is S Super Aqua of Electrolytic Liquid? 1.A.6 The Mechanism of Sterilization 1.A.7 The Sterilization Mechanism of Super Aqua B. The Bactericidal Effect Experiment of Superaqua 1.B.1 Description of the Experiment Content and Method 1.B.2 The Tried Bacteria Species in the Experiment 1.B.3 Outcome of the Experiment 1.B.4 Summary of the Experiment C. The Bactericidal Effect Experiment of Organic Compound Existing 1.C.1 Description of the Experiment Content and Method 1.C.2 1.B.2 The Tried Bacteria Species in the Experiment 1.C.3 Outcome of the Experiment 1.C.4 Summary of the Experiment D. The Storability Test of Super Aqua 1.D.1 Description of the Test Content and Method 1.D.2 Summary of the Test E. Animal Safety Test of Super Aqua 1.E.1 The Tested Items 1.E.2 Description of the Test Content 1.E.3 Summary of the Test F. The Report of Animal Safety Test of Super Aqua |
| 2. 提案編 A. 銀イオン水の利用法と銀イオン発生装置の設備方法 2.A.1 pHによる銀の変化 B. 水酸化銀機能水 2.B.1 銀イオン水グラフ C. アルカリ銀イオン水の静菌効果と食品としての安全性 2.C.1 銀ミネラル―食品としての安全性 2.C.2 アルカリ銀イオン水―食品保存性 2.C.3 アルカリ銀イオン水の静菌効果実験結果 D. データ開発課実験報告書 2.D.1 銀イオン水煮沸実験 E. アルカリイオン+水酸化銀機能水で長持ち(銀の安全性) 2.E.1 料理における銀の抗菌効果 2.E.2 銀の抗菌力を試す F. 電解酸化水およびアルカリイオン水の無添加食品加工への応用例-ゆでんどん保存性試験 2.F.1 月刊プラザの露出 2.F.2 ゆでうどん製造工程におけるソフト酸化水の殺菌効果の検討 2.F.3 試験検査成績書と食品報告書 G. 色々な応用データ-美味しさデータ H. アルカリイオン水と油の混合試験 2.H.1 電によるエネルギレベルの変化表 2.H.2 水の電気分解特性 I. なぜイオン水がクリーニングに良い結果を生むか? 2.I.1 アルカリイオン水はなぜ洗剤を1/3減少し、二次汚染を減少させる事ができるか 2.I.2 濯ぎの回数が一回で仕上る理由 2.I.3 酸性水による濯ぎが漂白及び劣化防止効果を生む理由 2.I.4 経済効果について J. 生命と還元電位 K. 出版品-比較薬局方 L. イクラ原卵の除菌処理へのソフト酸化水利用 2.L.1 試験検査報告書 M. ご提案-食品加工業、歯科医療、農業 2.M.1 食品加工業―「おいしさ長持ち」+「衛生管理」=「水でコストダウン」 2.M.2 歯科医療―スタッフの手洗い、消毒、器具の洗浄 2.M.3 農業―減(無)農薬のお手伝い |
2. Proposal Series A. The Utilization of Silver-ion and the Equipment Method of It 2.A.1 The Silver Changings According to pH B. Silver Hydroxide Functional Water 2.B.1 The Graph of Silver-ion Water C. The Bacteriostatic Effect Alkaline Silver-ion Water and the Safety of Alkaline Silver-ion Water Used as Drinking Water 2.C.1 The Safety of Silver Mineral Used as Drinking 2.C.2 The stability of Alkaline Silver-ion Water Used in Food Preservation 2.C.3 Outcome of the Bacteriostatic Effect Test D. The Reports of the Experiments and Tests from Data Development and Storage Division E. The Long-lasting Feature of Alkaline Ion and Acid Silver Water (The Safety of Silver) F. Super Aqua and Acid Silver Water Used in Additive-free Food Producing-The Stability Test of Boiled Udon 2.F.1 The Reveal in Plaza, a Monthly Publication 2.F.2 The Study of Superaqua’s Bactericidal Effect during the Boiled Udon Producing Process 2.F.3 Test-Inspection Report and Food Report G. Examples of Super Aqua Used in Food Industry H. The Test of Mixture of Alkaline-ion Water and Oil 2.H.1 The Table of Energy Changing Levels Coming up with the Change of Electricity 2.H.2 The Decomposition Characteristics of Water Electrolyzing I. Why Does Ion Water Make Good Effect in Cleaning? 2.I.1 Why Can Alkaline-ion Water Reduce the Usage of Lotion Which Also Reduces the Pollution? 2.I.2 Reasons Why You Can Easily Finish the Washing Process for Only Taking One-time 2.I.3 Why Can Super Aqua Have Whitening-effect and Prevent the Deterioration? 2.I.4 About the Cost Effectiveness J. Life and Reduction Potential K. Publication-比較薬局方 L. Super Aqua Used in the Sterilization Processing of Roe 2.L.1 Test Inspection Report M. Proposals─Food-processing Industry, Dental Care, Agriculture 2.M.1 Food-processing Industry─ “Long-lasting Palatability” + “Hygiene management” = Cost-down 2.M.2 Dental Care─the Hand-washing of Staffs, Disinfection, Cleaning of Equipments 2.M.3 Agriculture─Less (No) Use of Pesticides |
| 3. 食品編 A. ハイクロソフト酸化水とは 3.A.1 特徴 3.A.2 水質 3.A.3 革命的なコストダウン 3.A.4 Superaquaが注目されている理由 B. 食中毒の知識 3.B.1 食中毒事例集 3.B.2 食中毒はこうして起こる 3.B.3 主な食中毒菌 3.B.4 社会的責任 3.B.5 食中毒を防ぐには C. オムコからの提案 3.C.1 食中毒対策に~オムコからの提案 3.C.2 使用例‧データ集-手洗い効果 3.C.3 使用例‧データ集-まな板の除菌 3.C.4 使用例‧データ集-ミントの除菌 3.C.5 使用例‧データ集-フグ生肉殺菌試験(方法及び結果) 3.C.6 使用例‧データ集-ウインナーの除菌-電解酸化水およびアルカリイオン水の無添加食品加工への応用例-ポークウインナー保存性試験 3.C.7 使用例‧データ集-電解酸化水による洗浄試験-手指の洗浄、まな板の洗浄、食材の洗浄 |
3. Super Aqua Used in Food Industry A. What is Super Aqua ? 3.A.1 Features 3.A.2 Quality of the Water 3.A.3 Innovation For Cost-down Method 3.A.4 Why Does Everyone Keep an Eye on Super Aqua? B. Knowledge about Food Poisoning 3.B.1 Cases of Food Poisoning 3.B.2 Why Does Food Poisoning Occur? 3.B.3 Major Food Poisoning Bacteria 3.B.4 Social Responsibility 3.B.5 How to Prevent Food Poisoning? C. Proposals 3.C.1 The Proposal that We Suggest You How to Deal with Food Poisoning 3.C.2 Real Case─The Effect in Hand-washing 3.C.3 Real Case─Eradication of Chopping Board 3.C.4 Real Case─Eradication of Mint 3.C.5 Real Case─Raw Meat Sterilization Test of Puffer Fish (Method and Outcome) 3.C.6 Real Case─Eradication of Wiener─ 3.C.7 Real Case─Examples of Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water and Alkaline Water Used in Additive-free Food Processing─Pork Wiener Storage Stability Test 3.C.8 Real Case─The Washing Test of Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water─Finger-washing, Cleaning of the Chopping Board, Cleaning of Ingredient |
| 4. 医療編 A. 電解酸化水(新技術学術発表) B. 出版品-消毒剤の選び方と使用上の留意点 4.B.1 各消毒剤の特徴 C. 殺菌効果試験報告書 D. 電解水のMRSAに対する抗菌試験(エイズあり) E. ソフト電解酸化水 F. 金属腐食性検査報告 G. 内視鏡洗浄方法 H. ソフト酸化水実用編-手洗い、雑巾の洗浄、テーブル・トイレ等の清掃、床掃除 I. 機能水シンポジウム’95京都大会の資料 J. 第17回日本手術医学会の資料 |
4. Superaqua Used in Medical Field A. Electrolyzed Water-Super Aqua (Academic Announcement of New Technology) B. Publication- (Considerations on the Use and the Choice of Disinfectant) 4.B.1 Features of Each Disinfectant C. Report of Bactericidal Effect Test D. Antibacterial Test of Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water for MRSA(Here is Trump) E. Supera Aqua Electrolyzed Water F. Report of Metal Corrosion Inspection Test G. Practical Case of Super Aqua-Hand-washing, Cleaning of Wiper, Cleaning of Tables or Toilet, etc. H. Information from Symposium of Functional Water ’95 in Kyoto I. Information from the 17th Japan Surgery and Medicine Symposium |
| 5. 農業編 A. はじめに B. こんな農家の方におすすめです C. 酸化水はこのような形で農家の方々のお役に立ちます D. Superaquaの電解酸化水(ハ―ド酸化水、ソフト酸化水)について E. 主な作物の病害とその病原 F. ハード酸化水による植物病原菌に対する殺菌効果の検討 5.F.1 ハード酸化水による植物病原菌に対する殺菌効果の検討 5.F.2 ハード酸化水の抗ウイルス性の検討 G. 酸化水の農業への使用法 H. 酸化水を利用した栽培実用例 5.H.1 イチゴのハウス栽培 5.H.2 キュウリのハウス栽培 5.H.3 メロンのハウス栽培 5.H.4 日本なし I. 酸化水と農薬.展着剤との混合試験 J. 電解酸化水を利用した農業事例集 K. 使用例‧データ集-電解酸化水の農業利用(実用編)-日本梨栽培の栽培の実用例 L. 使用例‧データ集-肥育牛に関するアルカリ性電解カルシウム水供与が肉質に与える影響 M. 使用例‧データ集-アルカリイオン水給水による肥育肉豚の成長、血液性状および枝肉各付けへの効果 |
5. Superaqua Used in Agriculture A. Opening B. Super Aqua is Applicable for These Kinds of Farmers C. We Can Help Farmers in These Ways D. About Electrolyzed Water of Super Aqua E. Major Diseases of the Crop and the Causes F. Study of Super Aqua Water Used in the Disinfection Against Plant Pathogens 5.F.1 Report of Superaqua Water Used in the Disinfection Against Plant Pathogens 5.F.2 Study of the Antiviral Ability of Super Aqua Water G. Usage of Superaqua Water Employed in Agriculture H. Examples of Super Aqua Water Used in Cultivation Practices 5.H.1 Greenhouse Cultivation of Strawberries 5.H.2 Greenhouse Cultivation of Cucumbers 5.H.3 Greenhouse Cultivation of Melons 5.H.4 Japanese Pears I. Mixing Test of Super Aqua Water and Pesticides/Spreading Agent J. Examples of Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water Used in Agriculture Field Real Case—Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water Used in Cultivation —Cultivation of Japanese Pears K. Real Case—The Influence toward the Texture of Fattening Cattle Growth in which the Alkaline Electrolysis Calcium Water is Provided L. Real Case—The Growth of Hogs, the Flesh Connection Situation of the Hogs with Alkaline-ion Water Supplied |
Super Aquaに関する参考資料や公文書
Academic Papers, Comparison with Similar Items and Official Documents about Super Aqua
| Japanese/Chinese | English |
|---|---|
| 1. 検見報告 *酸化水 A. 2006/01/16 酸化水の細菌の抑制作用のテスト B. 2006/01/23 酸化水の細菌の抑制作用のテスト C. 2006/06/06 酸化水の細菌の抑制作用のテスト D. 2006/09/22 酸化水の細菌の抑制作用のテスト |
1. Scrutiny Reports * Super Aqua A. 2006/01/06 Bacteriostatic Action Test of Super Aqua B. 2006/01/23 Bacteriostatic Action Test of Super Aqua C. 2006/06/06 Bacteriostatic Action Test of Super Aqua D. 2006/09/23 Bacteriostatic Action Test of Super Aqua |
| 2. 学術ペーパー A. 在雞舍消毒上弱酸性次亞氯酸蘇打水的效果之檢討 B. 機能水藥劑對於飲料製造環境的微生物的殺菌效果 C. 酸化殺菌水用於水產品之清洗殺菌技術 |
2. Academic Papers A. Study of the Effect of Supe Aqua Used in Sterilization of Chicken Coop B. The Effect of Super Aqua Employed in the Sterilization of Microorganisms Existing in Beverage Producing Environment C. The Cleaning Sterilization Technology of Super Aqua Used in Aquatic Product |
| 3. 技術移転 A. 「酸化水」對於截切蔬菜汁殺菌效果之評估 B. 生鮮牡蠣與魚片之最適清洗殺菌之方法 |
3. Technology Transfer A. The Assessment of “Super Aqua” Used in Fruit and Vegetable Sterilization B. The Optimal Cleaning Method for Fresh Oysters and Fish |
| 4. 消毒について A. 消毒の基礎知識 B. 医療器械の滅菌や消毒 C. 物質安全資料表―塩酸 D. 物質安全資料表―次亜塩素酸ナトリウム |
4. About Disinfection and Sterilization A. The Basic Knowledge about Sterilization B. The Sterilization and Disinfection of Medical Devices C. Information Table about the Safety of Hydrochloric Acid D. Information Table about the Safety of Sodium Hypochlorite |
| 5. Superaquaにつて A. Superaquaの生成化学反応式について B. Superaquaの主成分―HOC1の説明 C. 殺菌水(Superaqua)の特色 D. Superaquaが各材料への影響の評価書 (酸化殺菌水とソフト酸化水) E. Superaquaの特色 F. 次亜塩素酸ナトリウム(漂白剤)の特色と欠点 G. 殺菌水(Superaqua)VS次亜塩素酸ナトリウム(漂白剤) H. 殺菌水(Superaqua)の次亜塩素酸ナトリウム(漂白剤)より優れたところ I. 殺菌水(Superaqua) VS強酸 J. 殺菌水(Superaqua)の二酸化塩素より優れたところ K. 殺菌水(Superaqua)のオゾン(O3)より優れたところ L. 殺菌水(Superaqua) VS一般の消毒剤 M. 食品上の殺菌原料比較表 N. 消毒殺菌剤の比較表 O. 殺菌水(Superaqua)の使用事例 |
5. About Superaqua A. About the chemical Reaction Formula of Super Aqua B. The Main Component of Superaqua-H0C1 C. Characteristics of Super Aqua Sterilization Water D. The Assessment Report of Super Aqua’s impact on Materials The Characteristics of Super Aqua Sterilization Water E. The Characteristics and Disadvantages of Sodium Hypochlorite (Bleaching Agent) F. Super Aqua Sterilization Water VS Sodium Hypochlorite (Bleaching Agent) G. What Are Super Aqua Sterilization Water Better than Sodium Hypochlorite (Bleaching Agent) H. Super Aqua Sterilization Water VS Strong Acid I. What Are Super Aqua Sterilization Water Better than Strong Acidic Water J. What Are Super Aqua Sterilization Water Better than Ozone(O3) K. Super Aqua Sterilization Water VS General Disinfectant L. Comparison Table of Sterilization Materials on Food Disinfection M. Comparison Table of Different Disinfecting Agent N. The Examples of Super Aqua Sterilization Water Employed |
| 6. Superaquaの設置装置について A. 装置システムの概念図 B. 貯水槽システム流程図 |
6. About The Device-setting of Super Aqua A. Conceptual Diagram of Super Aqua Device System B. The Flow Chart of the Water-storage-tank System |
| 7. 応用事例 A. CIP配管洗浄例 B. 殺菌水(Superaqua)への評価-微生物除去 C. 殺菌水(Superaqua)の殺菌力とコストダウン D. 無菌使用の事例-日本のペットボトル E. 21世紀での滅菌上の新突破 F. 殺菌水(Superaqua)-内視鏡 |
7. Examples of Super Aqua Usage Cases A. The Cleaning of CIP Pipe The Assessment of Super Aqua U Sterilization Water’s Microorganism Removal Ability B. The Bactericidal Power and Cost-down Ability of Super Aqua Sterilization Water C. Examples of Aseptic Working─the PET Bottle of Japan D. The New Breaking-through of Sterilization in 21th Century E. Super Aqua Sterilization Water─Endoscope |
| 8. 医療機関でのSuperaquaの応用 A. 医療界での使用範疇 B. 内視鏡の洗浄 C. 器具の洗浄 D. 病院内の清掃 E. Superaquaの生成装置 F. Superaquaを採用した日本の病院リスト(一部) |
8. Examples of Super Aqua Employed in Medical field A. The Territory where Super Aqua is Used in Medical Field B. Cleaning of Endoscopes C. Cleaning of Instruments D. The Cleaning Matters in the Hospitals E. The Generating Device of Super Aqua F. The List of Hospitals in Japan where Adopted Super Aqua (excerption) |
| 9. 他の参考資料 A. 医療・食品業でよく使われる殺菌剤 B. グルタルアルデヒド-OHC(CH2)3CHについて C. 食品工場の消毒剤-過酢酸について D. レイバル商品の参考資料 |
9. Other References A. The Most Used Disinfectants in Medical/Food Industry B. About Glutaraldehyde─OHC(CH2)3CH C. About the Disinfection Most Used in Food Factory─Peracetic Acid D. Reference Materials for Competing Products |
Superaquaに関する学術的資料
Academic Papers and Reports about Superaqua and Other Acid Water
| 見出し/Headline | English | Source/Institute |
|---|---|---|
| Reprocessing of Gastrointestinal Endoscopes of the Superaqua Electrolyzed Water | Medical Care Studios for Functional Water | |
| Cleaning and Disinfection of Endoscopes with Superaqua Electrolyzed Water | ||
| ハイクロソフト酸化水の病院での利用例 | Examples of (Super Aqua)Sterilization Water used in hospitals | |
| ソフト酸化水、セリウスソフト水の主な導入先(抜粋) | List of companies/institution where imported Super Aqua Water (excerption) | |
| 弱酸性電解生成溶液の使用経験 | Experience of Using Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | 第41回 日本透析医学会 |
| 透析患者褥瘡ケアー:弱酸性電解酸性水の効果 | Taking Care of Decubitus Ulcer: The Effect of Using Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | 第41回 日本透析医学会 |
| 電解酸化水を用いた透析室の殺菌 | Sterilization of Dialysis Room Using the Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | 第41回 日本透析医学会 |
| CAPDカテーテル出口部ケアの検討 | The Study of Maintenance of CAPD Catheter Outlet | 第41回 日本透析医学会 |
| ソフト酸化水によるCAPDカテーテル出口部洗浄の検討 | The Study of Cleaning of CAPD Catheter Outlet with Super Aqua Water | 第42回 日本透析医学会 |
| 透析施設における弱酸性水の有用性 | Usefulness of Employing Super Aqua Water in the Dialysis Facilities | 第43回 日本透析医学会 |
| 糖尿病性腎症のフットケア~足趾先端部の壊死に対する弱酸性水の温浴の効果 | Foot-care of Diabetes and Nephropathy: The Warm Bath Effect toward the Slough of Fore-end Feet | 第43回 日本透析医学会 |
| 当院CAPD患者におけるカテーテル出口部感染状況の調査と予防の試みについて | Investigation and Attempt for Prevention of Catheter Outlet Infection Situation of CAPD Patients in Our Hospital | 第43回 日本透析医学会 |
| 出口部感染に弱酸性水洗浄を試みて | In an Attempt to Clean the Outlet Portion Infection with Super Aqua Water | 第43回 日本透析医学会 |
| 機能水による透析装置洗浄を経験して | Experience of Dialysis Machine Washing with Functional Water | 医療法人永仁会 永仁会病院 腎センター |
| 弱酸性水對內視鏡再處理的應用 | The Application of Reprocessing the Endoscope with Super Aqua Water | 機能水醫療研究I(1):40-433,1999 |
| 機能水を使った消化器内視鏡洗浄及び消化器病変への応用 | Application of Function Water for Diseases of Digestive Organ | |
| 電解水による内視鏡機器の洗浄消毒のためのガイドラインの構築に向けて | Toward the Construction of Guidelines for Cleaning and Disinfecting Endoscopes Apparatus with the Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | NTT東日本関東病院 消化器内科 |
| 医療器具の消毒 | Cleaning and Disinfection for Medical Devices with Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | NTT関東逓信病 院臨床検査科 |
| 電解機能水による洗浄、消毒の有効性について -下部消化管内視鏡を中心に- |
Washing with Electrolyzed Functional Water, about the effectiveness of disinfection─Around the Lower Digestive Tract Endoscope─ | 宇治徳州会病院 内視鏡センター |
| H.pyloriに対する上部消化管内視鏡の簡易洗浄法の検討 | The Study of Simple Cleaning Method of the Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscope toward H.pylori | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| 内視鏡鉗子孔の強酸性電解水を用いた噴射式洗浄法の有効性について--一般細菌に対する殺菌消毒効果 | About the Effectiveness of Cleaning the Forceps Hole of Endoscopes with Injection Type Cleaning Method(Strong Acid Water Employed) | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| 強酸性水のHBVに対する効果-上部内視鏡検査における検討- | The Effect on the HBV of Strong Acid Water - Study of Upper Endoscopes | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| アルカリ水、超酸性水を使用した内視鏡洗滌、消毒について | About the Cleaning and Disinfection of Endoscopes Using Strong Acidic Water | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| スコープ簡易再処理における、強酸性水の有用性 | The Usefulness of Strong Acid Water Used in the Simple Reprocessing of Scopes | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| ミンテック社自動内視鏡再処理装置(AER)に弱酸性水を試用して | Using Superaqua Water on Automatic Endoscope Reprocessor(AER) of Mintekku Inc. | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| 内視鏡洗浄消毒装置「クリーントップ」の使用経験 | Experience of Using “Clean-top”, the Disinfection Device for Endoscopes | 日本消化器内視鏡技師会 抄録40 |
| 血液透析における弱酸性電解水の実際-過酢酸+過酸化水素1%液による洗浄効果の検討 | Truth of Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water Used in Hemodialysis – Study of the Cleaning Effect of Peracetic Acid + Hydrogen Peroxide | 第5回 HDF学会抄録 |
| 上部消化管内視鏡の検査間における洗浄・消毒法の検討 (ソフト酸化水の有効性) |
The evaluation of technique for cleaning and disinfection the panendoscope after use.—The effect of Superaqua electrolyzed water— | |
| 酸性電解水による内視鏡器具の消毒 | Disinfection of endoscopes using Super Aqua electrolytic water. | 大阪大学大学院医学系研究科 病態情報内科学 |
| 酸性電解水による消化管内視鏡の再処理 | Reprocessing of Gastrointestinal Endoscopes by the Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | 亀田メディカルセンター 内視鏡室 |
| 医療における機能水の現状と展望:適用内・適用外使用 | Trends and Perspectives of Functional Water Research in Medical Field: Applicable and Inapplicable Use of Strongly Acidic Electrolyzed Water | NTT東日本関東病院 臨床検査部 |
| 酸性電解水による内視鏡消毒 | Endoacopy Disinfection With Super Aqua Electrolyzed Water | NTT東日本関東病院 内視鏡センター |
<参考用比較資料>強酸水に関するペーパー <For Comparison>Papers about Strong Acid Water
| 見出し/Headline | English | Source/Institute |
|---|---|---|
| 強酸化及び強アルカリ機能水による血液透析回路における各種チューブ類洗浄効果 | The effect of alkaline and acidic/oxidative functional water on clinical use as washing solution of connecting tubes in hem dialysis circuit. | |
| 強酸性電解水による血液透析装置の洗浄消毒 | Cleaning and disinfection of the blood dialysis equipment by the electrolyzed strong acid aqueous solution(ESAAS) | |
| 強酸性電解水の血液浄化(透析)装置の洗浄消毒への応用 ~利点と問題点~ |
Application of Electrolyzed Strong Acid Aqueous Solution to Cleaning and Disinfection of Blood Cleaning(Dialysis) Equipment-Advantages and Problems | |
| 強酸性水と内視鏡の洗浄消毒 | Electrolyzed Water and Endoscope Disinfection | NTT関東逓信病 内視鏡センター |
| 強酸性水を使用した効率的な内視鏡洗浄消毒法 | Effective cleaning and disinfection of endoscopes with Super Aqua electrolyzed water | NTT関東逓信病 内視鏡センター&臨床検査科 |
| 強酸性水による内視鏡の洗浄・消毒の経験 | Irrigation and disinfection of endoscope using acid water | 北里大学東病院 内視鏡科 |
| 内視鏡消毒における強酸性水の有用性 | The Usefulness of Function Water for Disinfection of Endoscope | 大阪大学病態制御外科& 東京都立駒込病院 |
| 強酸性電解水使用における透析機器の維持管理 | Maintenance Management of the Hem dialysis Equipment in Strongly Acidic Water use | 医療法人紀陽会田仲北野田病院 |
| 強酸性電解水を使ったオーバーフロー式 全自動内視鏡洗浄消毒装置(KE-2000)の開発 |
Overflow Type Using Acid Electrolyzed Water -the Development of KE-2000(Full-automatic Disinfection Device for Endoscopes)- |
|
| Helicohacter pyloriの内視鏡消毒に対する強酸性電解生成水の有用性 | The Disinfective effect of electrolyzed strong acid aqueous solution on a gastro-endoscope to prevent Helicobacter pylori transmission |
Superaquaの殺菌検査結果の報告 Reports of the outcome of Superaqua used in Sterilization
| 見出し/Headline | English | Source/Institute |
|---|---|---|
| ソフト酸化水の殺菌効果試験 | Bactericidal Effect Test of Super Aqua Water | 東京女子医科大微生物免疫学教室 |
| 殺菌効果試験 | Experiments of Bactericidal Effect | 財団法人日本食品分析センター |
| ソフト酸化水動物安全性試験結果報告 | The Report of Animal Safety Test in Super Aqua Water | 財団法人食品農医薬品安全評価センター |
Remarks: The above major data were provided by President Okazaki T.
- For better understanding and avoid the confusing the name of productions which used in following data or Academic Papers or different test or studies etc We have revised and use the name of “ Super Aqua” due to it is the most same productions related our technology.
- Above data information or topic are mainly providing to our customers for further reference.
Introduction of Super Aqua new-generation sterilization techniques
The Statement
The functions, features, or applications of the hypochlorous acid or its products on this website are described in usages or actual cases is for reference only. If the application may involve medical application or efficacy, effectiveness etc., should based on the doctor's judgement. We request our client to apply for relevant certification to your Health Authority in accordance with your relevant laws and regulations in each country. We would like hereby declare the above matters.
1. Technical background of Super Aqua
(1) 1,000 patents over 40 years:
The know-how of Super Aqua for electrolyzed functional water were originally developed from Okazaki Manufacture Technology (OMT) which has been researching electrolyzed functional water for four decades and owns 1,000 industry-leading patents and techniques.
The 100% hypochlorous-acid liquid is the core technique first developed by Chiarman T. Okazaki, from Okazaki Manufacture Technology (OMT) and a revolutionary product changing the history of sterilization and contributing to the Earth as well as human and environmental health.
(2) Industrious applications:
The technique of hypochlorous-acid liquid has attracted attentions from different industries including more than thousands of foods & beverages manufactures and medical institutes for its applications, for example, many brewery,food,beverage 、national hospital、and dental clinics. The technique has potentials for applications to various industries in the future.
1、History of functional sterilizing water
First generation: sodium hypochlorite (bleaching water)
High-concentration sterilizing water, a.k.a. sterilizing king
Original sodium hypochlorite liquid: concentration>12%; pH>12
Advantages:
- Strong antibiosis and efficacy (condition: high concentration)
- Fewer residues; safety at low concentrations
- Economy; wide applications
Disadvantages:
- Transformation to alkalinity after increase of the concentration
- Detrimental to skin and mucous membrane
- Strong metal corrosion degrading rubber or plastic
- Dilution of original liquids before use (danger)
∇
Second-generation: functional sterilizing water
Strong-acid water; high efficacy; instability
(The functional sterilizing water is derived from electrolysis in salty water.)
- Corrosive substance
- Chlorination
- Degradation attributed to organics
Concentration of hypochlorous acid=10~50ppm (0.001~0.005%); pH<2.7
Advantages:
- Low-concentration available chlorine (hypochlorous acid) with strong sterilization effect on many bacteria
- No residue
Disadvantages:
- Available chlorine (hypochlorous acid)
- Strong metal corrosion
- Sterilization effect degraded due to existence of few organics
- Chlorination
∇
Third-generation: Super Aqua sterilizing water
Optimized sterilizing water: 100% hypochlorous-acid sterilizing water
Low concentration; high efficacy; concentration of chlorine <1ppm
Concentration of hypochlorous acid (electrolyzed)=50~80ppm (0.005~0.008%); pH=4.0~7.0
Concentration of hypochlorous acid=100~200ppm/500ppm (0.01~0.05%); pH=4.5~6.5
Free effective chlorine for sterilization effect is molecular hypochlorous acid.
Advantages:
- High-concentration hypochlorous acid (50~80ppm or 100/500ppm)
- Safety: chlorinated sterilizing water<1ppm
- Environment-friendly: sterilizing water reduced to water and trace salt
- HACCP/GMP certificates
- High safety and low metal corrosion
- Wide applications
2、Animal safety test report
| Acute toxicity test | No abnormality |
|---|---|
| Single skin irritation test | No irritation |
| Eye irritation test | No irritation |
| Multiple skin irritation test | No irritation |
| Sensibility test | Inaction |
| Cytotoxicity test | No trouble |
| Mutagenic activity test | No mutagenicity |
<Inspector: Public Interest Incorporated Foundation BioSafety Research Center,Japan (BSRC)>
3、Concept, sterilization effect and safety of sterilizing water
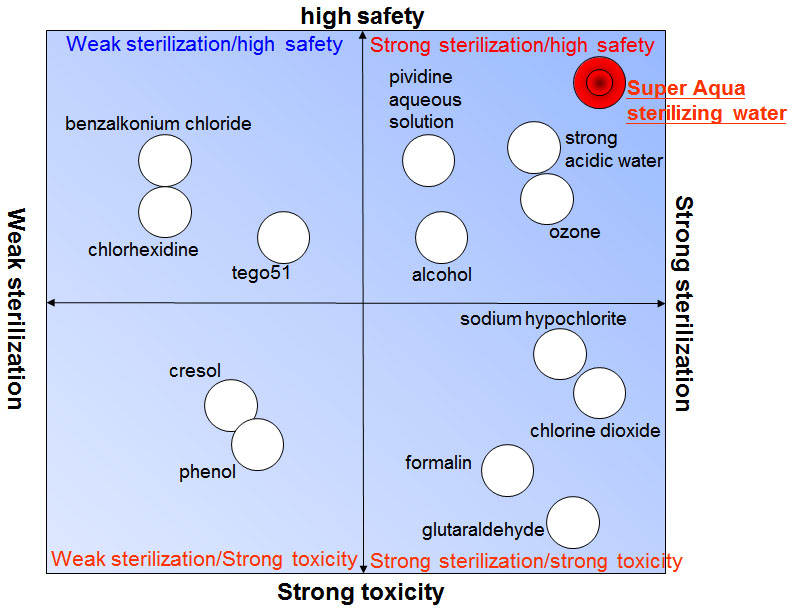
Concept, sterilization effect and safety of sterilizing water
- The conventional disinfectants are characteristic of good effect but strong toxicity or good safety but poor effect usually, i.e., two properties contrary to each other.
- Strong-acid water and ozone water which features good effect and high safety compared with the conventional disinfectants can be taken as an ideal solution.
- Super Aqua sterilizing water, which is free of the problems of strong-acid water and ozone water such as gasification of active ingredients and corrosion, is the first priority of a customer for sterilization.
4、Sterilization effect of free effective chlorine
Chemical reaction: H2O+Cl2
- Hypochlorous acid (HClO)---→free effective chlorine
- Hypochlorous acid ion (ClO-)↗
- Chloride ion (Cl-)→ No sterilization effect (e.g., seawater)
Free effective chlorine with sterilization effect
The comparisons for hypochlorous acid with different pH values are shown as follows:
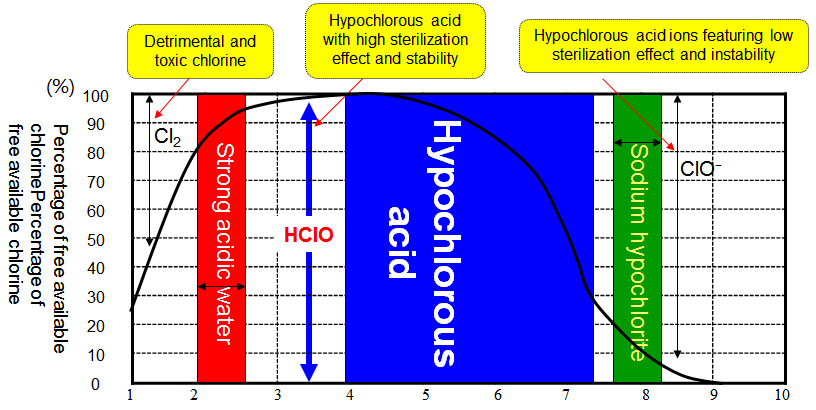
Literature: “Technique of Clean Water”, Norihito Tambo & Koichi Ogasawara, Gihodo Shuppan Co. Ltd., 1985
5、Sterilization effect of HClO (hypochlorous acid) which is 80 times as much as that of ClO- (hypochlorous acid ion) theoretically
Comparisons of sterilization effect between Super Aqua sterilizing water and sodium hypochlorite
Time to destroy 99% of E. Coli (unit: minute)
Example: Time to kill bacteria with 0.1 mg/L chlorine
| HClO | About 1.5 minutes (benchmark=1) |
|---|---|
| ClO- | About 120 minutes (80 times) |
| NH2Cl | About 520 minutes (350 times) |
Source: Environmental Protection Administration (EPA), U.S.A.
6、Sterilization effect tests of sterilizing liquids
| Names of Bacteria | Total Plate Count (1 ml) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial count | After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | |
| Escherichia Coli | 4.3×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 4.3×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4.5×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 4.5×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| MRSA | 3.4×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 3.4×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| Salmonella | 3.4×105 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 3.4×105 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1.6×105 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 1.6×105 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| Streptococcus | 1.9×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 1.9×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| Bacillus | 4.6×106 | 3.7×105 | <10 | <10 |
| 4.6×106 | 4.4×106 | 4.5×106 | 4.5×106 | |
| Candida | 2.3×106 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 2.3×106 | 4.4×106 | 4.5×106 | 4.5×106 | |
| Aureobasidium pullulans | 2.0×105 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 2.0×105 | 2.0×105 | 50 | <10 | |
Pink ground: Super Aqua sterilizing water residual chlorine: 57 ppm
White ground: sodium hypochlorite effective concentration: 200 ppm
* Initial count: Microbial count for no sterilizing water added
* <10: detection limit (no bacteria detected)
Super Aqua hypochlorous-acid liquid generator
Best Welcome® Hygiene Management Series
The air may have different bacteria, molds, etc. due to the environment or conditions. Even in the sterile room of the food and beverage factory, it is inevitable that the bacteria will be brought into the sterile room due to the entry and exit of the workers, causing the bacteria to grow, leading to product quality problems. In high-density farming environments such as raising pigs, cattle, chickens, ducks...etc, the spread of pathogenic bacteria will cause the animals to become sick or die and cause economic losses to the operators; public places where people enter and leave, such as hospitals, clinics, school tutoring classes, hotels. At the station, pathogens may be scattered in the air and affect human health.
In order to maintain customer health, deodorization of public space (deodorization) and clean, safe and sanitary production workshop, clean livestock environment, suitable planting environment, create a healthy and safe environment, use Super Aqua sterilization Technology and High-Efficiency Patented Ultrasonic Spray System for Sterilization is the best choice for hygiene management.
-
Commodity (A) Super Aqua High Concentration Environment Friendly Sterilizing Water SA-2100 series
-
Commodity (B) Patent/Waterproof High-Efficiency Ultrasonic Sprayer Series (spray particle size approx. 1-5 μm)
Super Aqua-Best Welcome® Hygiene Management Series
◇ Commodity (A) Super Aqua High Concentration Hypochlorous Acid SA-2100 Series
Super Aqua Sterilization Technology

Super Aqua SA-2100 sterilizing liquid mainly contains high concentration of hypochlorous acid. It is a food additive fungicide announced by the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Taiwan. It is harmless to the skin mucous membrane and has a safe and effective bactericidal effect. It can be sprayed safely in environment with or without people. Low residue, instant sterilization, and due to ultra-fine particle spray, it has a highly effective bactericidal effect on space bacteria.
◇ Super Aqua Sterilization Technology Products
| Super Aqua Hypochlorous Acid Sterilizing Solution 2L | Super Aqua Hypochlorous Acid Sterilizing Solution 5L | Super Aqua Hypochlorous Acid Sterilizing Solution 25L |
Product Instructions:
- Dishes / chopping board / kitchen knife / dining table, rag / towel: sterilization and deodorization
- Waiting room / inspection room / opening room to prevent hospitals from falling down.
- School Parenting Classroom: Sterilization, Avoid Contagion
- Toilet / kitchen waste: deodorization
- Floor / wall / handrail
- Pet cage, pet grooming workbench
- Use after pet bathing or pruning: sterilization, deodorization
Detailed Instructions: http://www.superaquaholding.com/index.php/en/sterilization-product-usage-en.html
◇ Product (B) Patent / Waterproof High-Efficiency Ultrasonic Sprayer Series (spray particle size of about 1-5 μm)
Eight Major Characteristics:
- Waterproof design: The sprayer is waterproof (patented) as a whole, which can avoid rust or short circuit failure of the machine under high humidity environment.
- Integrated fog module (patented): This integrated fog module can efficiently produce ultra-fine spray with higher fogging efficiency and effect.
- Waterproof fan (patented): Prevents short-circuit of the sprayer's fan in high humidity environment.
- New power box waterproof design (patented): It can prevent the humid air from entering the power box and causing machine failure.
- Liquid liquid tank (HCLO) floating liquid level design (patent): This patent design replaces the general induction type to avoid induction failure and make the supply of sterilization liquid more stable.
- Overheating and foolproof design: If the temperature of the sprayer exceeds 60 degrees Celsius, it will automatically stop running. After the temperature is lowered to 55 degrees Celsius, it can be restarted.
- Energy saving, low power consumption: Low voltage and high efficiency ultrasonic design, the cost of water and electricity for about 12 hours is only about US$0.3 (Note: depending on the model and Taiwan standard), it has energy saving effect.
- Can be operated for a long time: The sprayer can run continuously for 24 hours.
 |
 |
 |
|
| Model | SA-1801 | SA-3002 | SA-6003 |
| Specification | D35*W22*H36cm | D38*W28*H33cm | D38*W28*H33cm |
| Rated Voltage | AC110V/60HZ or AC220-240V/50-60HZ | ||
| Power Consumption | 160W | 240W | 480W |
| Output Current | 1.9AMP | 3 AMP | 6 AMP |
| Amount of Spray | 1.8 L / hr | 3 L / hr | 6 L / hr |
| Spray Particle Size | 1μm~5μm | ||
| Spray Range | 355.83 sq. ft. | 711.66 sq. ft. | 1423.33 sq. ft. |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Model | SA-9001 | SA-12001 | SA-18002 |
| Specification | D65*W42*H33cm | D76*W42*H33cm | D90*W45*H35cm |
| Rated Voltage | AC110V/60HZ or AC220-240V/50-60HZ | ||
| Power Consumption | 720W | 960W | 1440W |
| Output Current | 9 AMP | 12 AMP | 15 AMP |
| Amount of Spray | 9 L / hr | 12 L / hr | 15 L / hr |
| Spray Particle Size | 1μm~5μm | ||
| Spray Range | 355.83 sq. ft. | 711.66 sq. ft. | 1423.33 sq. ft. |
Super Aqua hypochlorous-acid liquid generator series
Super Aqua hypochlorous-acid liquid generator:
Super Aqua / HACCP MAKER Ⅱ series:

BW-300 series (entry level)
BW-300 series are entry-level hypochlorous acid generators hung on walls.
For example, hypochlorous acid generators can be hung on various locations such as kitchen, shop, school, nursing home, charity, hospital and backyard.
The hypochlorous acid generator is the best sterilizer installed at the location in which bacteria or viruses propagate.
BW-300 series include three models:
- BW-310 (no-power)
Despite the supply of specific solution displayed on the pressure gauge of BW-310, and specific method in the tank should be checked visually.
- BW-320 (standard)
The warning indicator for the generator short of specific solution or specific method is lit, if necessary. However, water is kept running.
- BW-330 (water-stop)
The supply of water is terminated and the warning indicator is lit when the generator is short of specific solution liquid or so on.
The supply of water to each of BW-300 series is controlled by the faucet. The water flow cannot be controlled by the extra faucet installed at the outlet.
Do not install extra fittings in the front of an accessory’s nozzle.
The vertical position of the outlet of a hose which is installed optionally should be lowered than the bottom of the hypochlorous acid generator body. Moreover, the specific solution will be influenced by the vertical position of the hose’s outlet which is lower than the bottom of the hypochlorous acid generator body.
For detailed information of BW-300 series, please click here.
The “emergency kit” for BW-310 is available in any emergency condition.
The emergency kit to which water is supplied via a normal hose is used to product sterilizing water conveniently with stored water in emergency conditions such as water and power outage.
For detailed information of the emergency kit, please click here.

BW-1500 SERIES (STANDARD)
With the output flow of 25 liters per minute, the standard BW-1500 supplies water as a normal faucet.
BW-1500 can be used in any place such as food processing factory and hospital.
With water distributed to multiple outlets, BW-1500 allows each outlet to be equipped with a faucet by which sterilizing water is controllably supplied.
There are three HCLO concentrations in each of the standard BW-1500 series, i.e., 50, 100 and 200 ppm, which are available via the touch-switching mode. (The three HCLO concentrations can be modified by the manufacturer before delivery.)

BW-4000 SERIES (HIGH-CAPACITY) (4,000 Liters per hour )
BW-4000 series are high-capacity hypochlorous acid generators with the output flow of 65 liters per minute, i.e., 4 ton per hour, for a venue to be sterilized with a great quantity of sterilizing water.
BW-4000 series, which are similar to BW-1500 series, allow an outlet to be equipped with a faucet.
There are three HCLO concentrations in each of the high-capacity BW-4000 series, i.e., 50, 100 and 200 ppm, which are available via the touch-switching mode. (The three HCLO concentrations can be modified by the manufacturer before delivery.)
For detailed information, please click here.
SUPER AQUA-2 for producing HCLO water

Super Aqua-2 is one device to dissolve specific solution in water for producing HCLO water.
A user who has owned the equipment for addition of specific solution so that able to use this solution water mix with the specific method for producing the hypochlorous acid liquids.
Moreover, after specific method generate with the raw water by Super Aqua-2, the sterilizing water with a certain HCLO concentration is produced with solution water which added into the Super Aqua-2 generator in which multiple HCLO concentrations can be producing and available.
For detailed information, please click here.
Fanslly-800 Hypochlorous Acid Powder Series
Fanslly-800 Hypochlorous Acid Powder,
Easily Transform Water Become Hypochlorous Acid!!
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1 gram | 2 grams | 3.2 grams | 500 grams | 1000 grams |
NMR Scientific Certification for Small-molecular Water Cluster
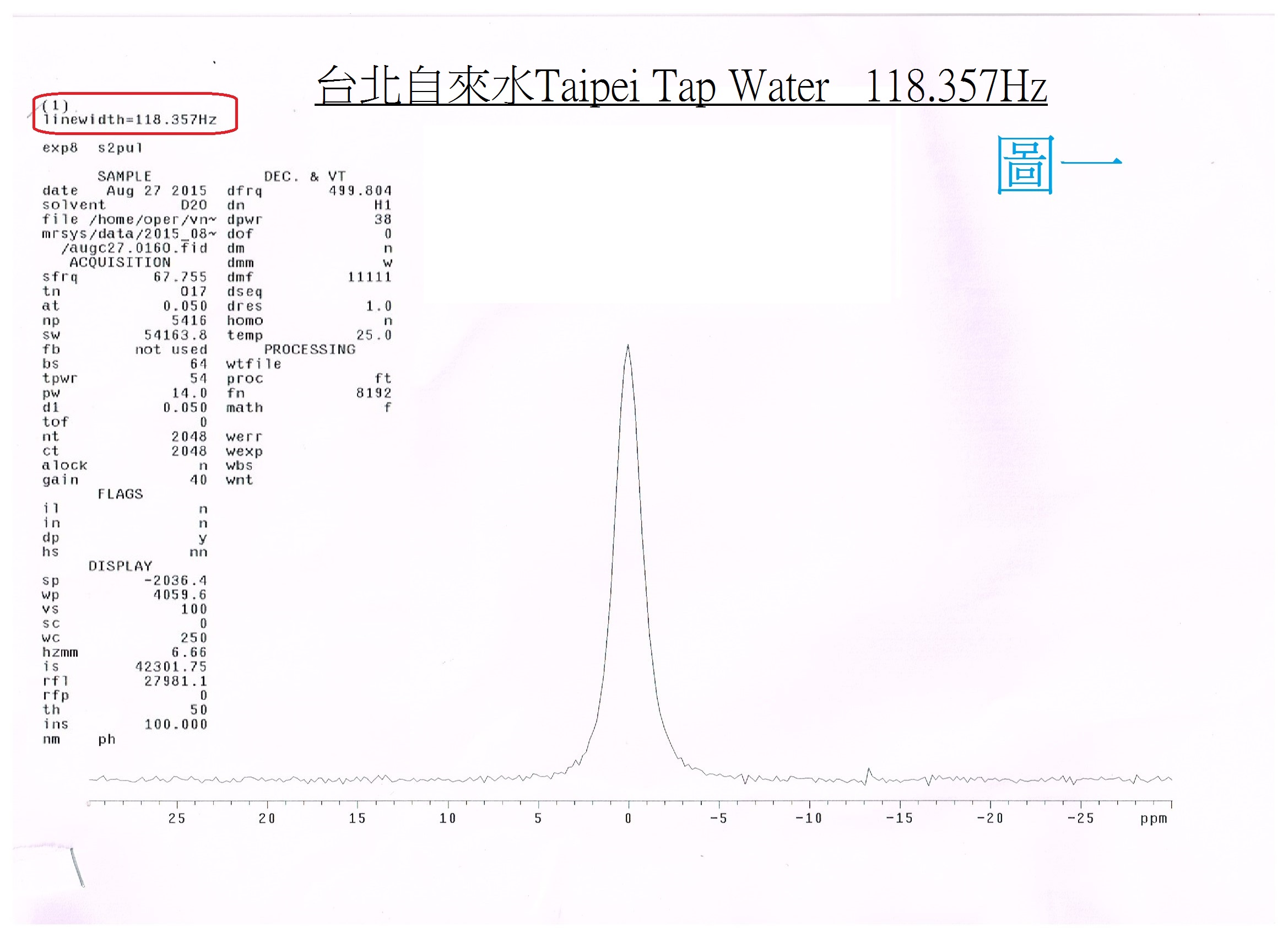
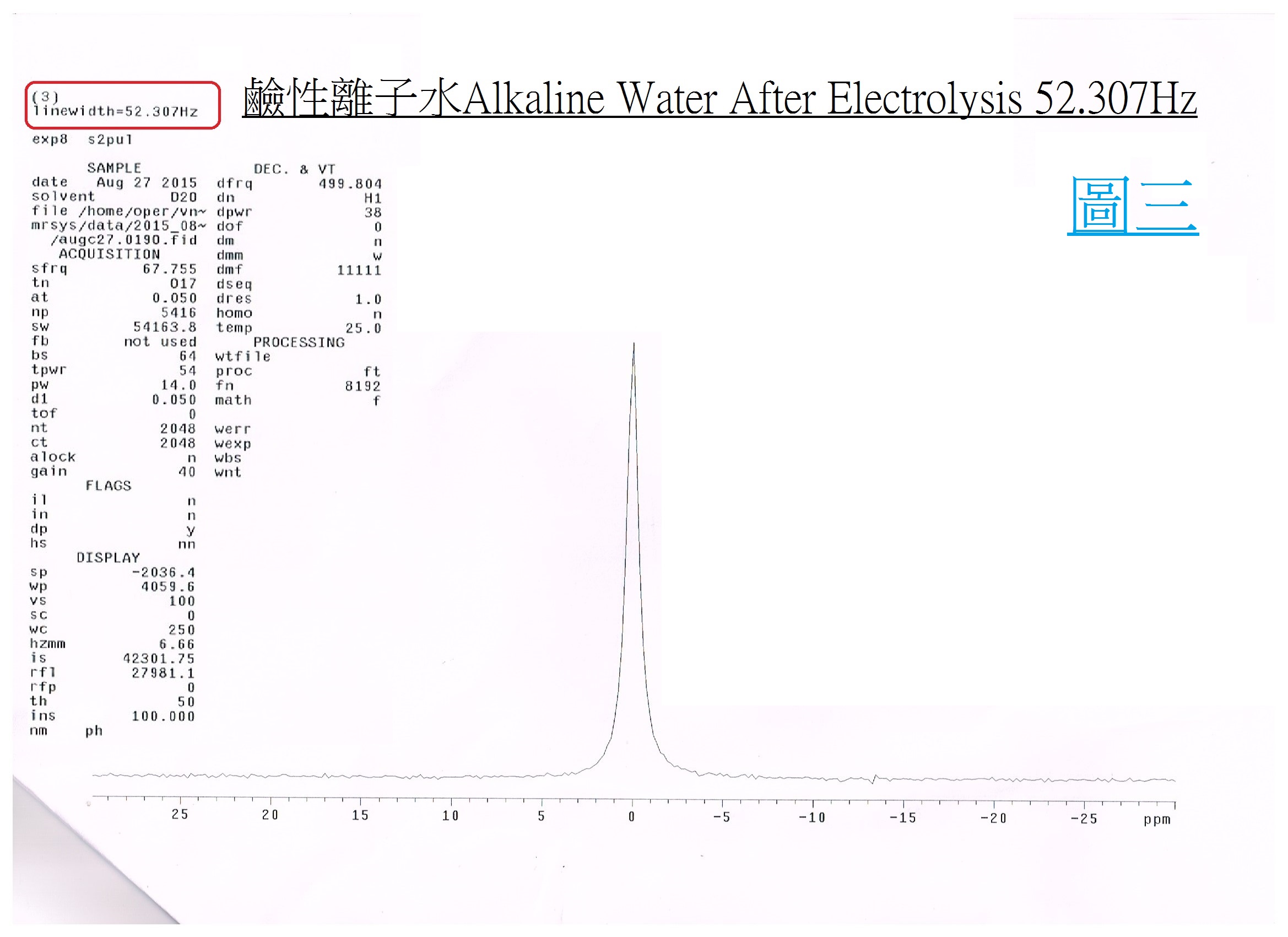
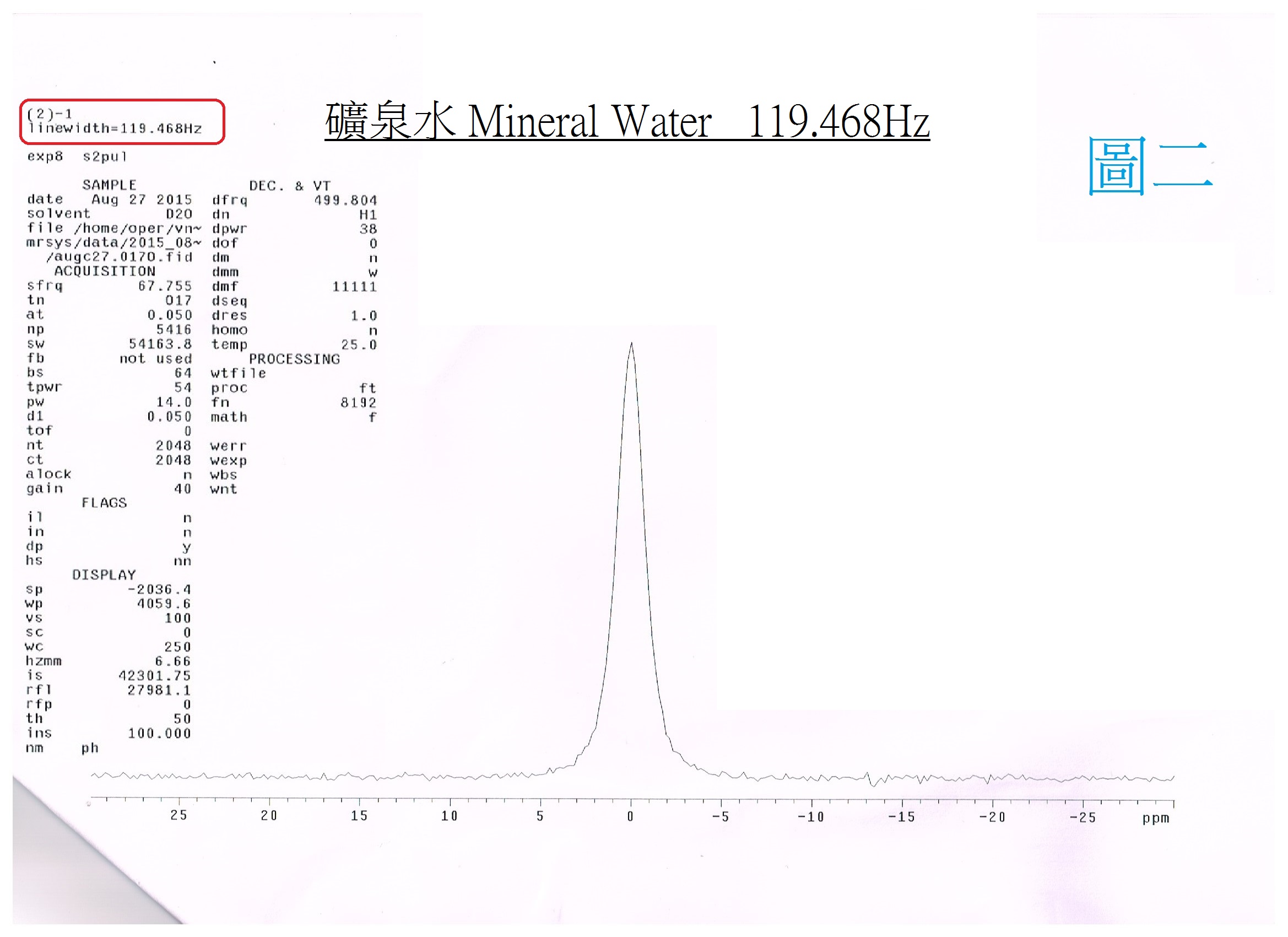
Small Cluster Water:Electrolyzed reduced water (alkaline ionized water) has been verified as small-molecular cluster water according to the NMR spectrometer. |
The alkaline ionized water is small cluster water, which can be measured by the NMR (Nuclear magnetic resonate spectrograph): the tap water is about 118Hz (PIC. 1); The mineral water is about 119Hz (PIC. 2); and the pH9 of alkaline ionized water (PIC. 3) is about 52Hz. |
|
During the electrolysis process, the water molecules will be recombined to small cluster water.
Easily absorbed by human body, the water with small cluster water is helpful for metabolism and can remove acidic substances and wastes from human body, therefore enhancing the inner environmental system, properly adjust the acidic physical condition and improve our health! |
Equipment for Alkaline Ionized Water
Technical features of Golden Alkalizer
Alkaline Ionized water: about 3,000L/hr
Acidic Ionized water: about 1,000L/hr
Comparisons of All Types of Bottled Drinking Water
|
Item Type |
Manufacturing process | pH value | Mineral | Water molecule cluster * Note 1 |
Water molecule (NMR) * Note 2 |
Taste (molecule cluster and hardness) |
Health Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline ionized water | (1) RO water + minerals→ electrolysis (2) natural water → electrolysis |
Alkaline (pH=9~9.5) |
Ionized minerals | 6 | Small (45Hz~55Hz) (depending on pH values) |
Palatable (Making tea or coffee, cocktail, cuisine, etc.) |
Small-molecule water active hydrogen (hydrogen) hydrogy ion Ca(OH)2 ionized minerals |
| Natural mineral water natural water |
Mountain spring groundwater |
Weak alkaline or acid (pH≒7.5) |
Natural minerals; natural minerals with trace elements |
8~12 (depending on locations and water conditions) |
94Hz (depending on locations; 80Hz (Village of Long Life)) |
Tastes depending on hardness and water molecule clusters are different from one another. | Natural minerals; trace elements |
| Mineralized drinking water | Tap water → RO water + artificial mineral | Acid (pH≒6.5) |
Pure water with artificial minerals added | 8~10 | 88Hz~90Hz in general (RO water) |
Palatable | Small-molecule water minerals |
| Pure water distilled water |
Groundwater or tap water → RO water or distillation processing |
Acid (pH≒6.0) neutral or acidic (distilled water) |
Nil | 8~10 13~15 |
Pure water: 88-90Hz; distilled water: 140Hz |
Good taste for pure water (no hardness); taste worsen for distilled water with larger molecule clusters |
It is not healthy to drink pure (distilled) water for a long period. * Note 3: The small-molecule water with little mineral is not healthy. |
|
* Note 1: Data of Kazuhiro Matsushita, JEOL |
 English
English  繁體中文
繁體中文  简体中文
简体中文