|
| LEADER OF ELECTROLYSIS TECHNOLOGY |
Approximate 100% Air Disinfection and Sterilization Effect
- Fanslly-800 Sterilization Test Report
- Approximate 100% Air Disinfection and Sterilization Effect
International renowned testing organization INTERTEK testing Fanslly-800 Hypochlorous Acid Liquid sprayed by SuperAqua Dry Mist Sprayer, it can reduce bacteria by 99.44% and fungi by 96.55% in just 1 minute. The effect is so amazing, see. - SuperAqua versus Epidemic Prevention
- Super Aqua Products for Disinfection
Latest News
-
Anti-Epidemic Fanslly Donate Fans...
The epidemic alert has lowered down to level 2 would cause increase demand on sterlizer especially in public venue and household, ...
SGS: Skin-friendly Hypochlorous Ac...
There are so many hypochlorous acid products in the market, how to choose? One is safe to body, and the other is...
Sanjay Dutt, Super Aqua's user
Sanjay Dutt, the Indian award winning movie star, met SuperAqua's epidemic prevention in year 2020. Noted on Fanslly-800...

Alkaline Ionized Water
Alkaline ionized water is alkaline water produced by an alkaline ionized water device (a.k.a. alkaline ionized water generator) from raw water directly and also electrolyzed reduce water known to the public. Alkaline ionized water is scientifically defined as the “weak-base low-voltage micro-molecule drinking water” (or the “reductive water” in Japan).

Super Aqua new-generation sterilization technique
The 100% hypochlorous-acid liquid is the core technique first developed by Mr.Tatsuo Okazaki, President of Okazaki Manufacture Company (OMCO) and a revolutionary product changing the history of sterilization and contributing to the Earth as well as human and environmental health.

OEM/ODM equipment
Superb background for electrolysis technologies and 1,000 patents in 40 years
Super Aqua follows a customer’s expectations or demands to design customized series of products: Household electrolyzers series (with filters included), commercial electrolyzers series, electrolyzed hypochlorous-acid liquid generator series, and ancillary equipment series.
新世代殺菌技術
History of hypochlorous acid
2、History of hypochlorous acid
1. History of hypochlorous acid
The strong sterilization effect of hypochlorous acid (HClO) was known to the elder generations.
Hypochlorous acid is a good bactericide with three characteristics as follows.
- Strong and quick sterilization effect in low-concentration dosages
- Little residue; hypochlorous acid liquids rinsed with water
- No trihalomethane generated
Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) stems from hypochlorous acid (HClO) which contains hypochlorous acid ions (ClO+) accounting for 90%. (As shown in the figure (top), the sterilization curve is drawn at the top.) Hypochlorous acid ions with little sterilization effect combine hydrogen ions (the molar ratio of hypochlorous acid ions to hydrogen ions=1:9) to become hypochlorous acid for sterilization. That is, sterilization is a slow process. Thus, hypochlorous acid ions are remained significantly.
Comparatively, weak-acid sodium hypochlorite contains hypochlorous acid ions (10% only) and hypochlorous acid for sterilization mostly. Thus, sodium hypochlorite features quick sterilization effect and little residues.
Moreover, trihalomethane which is a problem related to sodium hypochlorite is generated in alkaline environment rather than acidic environment.
There are two reasons which result in hypochlorous acid unpopular.
- Difficulty in manufacturing (poor stability and diseconomy)
- Difficulty in storage
That is, hypochlorous acid is produced difficultly and not stored for a long period.
2. Hypochlorous acid is produced in electrolysis first.
There are three methods shown as follows:
- Electrolysis of saline solutions: By using salt water for producing strong acidic water but the HCLO is unstable.
- Electrolysis of saline solutions in which HCl is mixed for production of hypochlorous acid (weak acid).
- Electrolysis of water in which HCl is mixed for production of hypochlorous acid (weak acid).
Each of the methods has specific advantages but is uneconomic because of consumable platinum (titanium) electrode plates expensive.
3. Hypochlorous acid – the key element of sterilization!
Hypochlorous acid (HClO), which is similar to ozone or chlorine dioxide, is capable of resolving and killing bacteria (viruses) in oxidation. However, hypochlorous acid unlike alcohol does not induce antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
In addition, hypochlorous acid which has no toxicity of ozone or chlorine dioxide is a mild bactericide for human beings.
Hypochlorous acid (HClO) vs. sodium hypochlorite
The sterilization effects of hypochlorous acid (pH=5.2; chloride concentration=57ppm) and sodium hypochlorite (pH=9; chloride concentration=200ppm) are compared and shown in the table (below).
The sterilization effects of hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus are similar; however, the sterilization effects of hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite on Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus) and mold are significantly different.
As shown in the table, hypochlorous acid has characteristics such as good sterilization effect and fast-acting property.
| Tested strains | Microbial content | Hypochlorous acid | Sodium hypochlorite | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloride concentration=57ppm; pH5.2 | Chloride concentration=200ppm; pH9 | ||||||
| After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | ||
| Escherichia Coli | 4.3x106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4.5x106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Bacillus subtilis | 4.6x106 | 3.7x105 | <10 | <10 | 4.4x106 | 4.5x106 | 4.5x106 |
| Aspergillus niger | 2.0x106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | 2.0x105 | 50 | <10 |
<10: no microbe detected; test temperature=23°C (Japan Food Research Laboratories)
The sterilization effect of hypochlorous acid (pH=5.2; chloride concentration=80ppm) on bacteria is shown as follows.
There is no bacterium detected after one minute.
It can be seen that all bacteria and viruses are eliminated by hypochlorous acid.
※Note: These results are test data from experiments only because hypochlorous acid reacting with other organic matters is consumed. In practice, new hypochlorous acid should be added frequently for a constant concentration.
| Tested strains | Testing liquid | Microbial content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Escherichia coli | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bacillus subtilis | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Salmonella | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bacillus cereus | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| MRSA | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Legionella pneumophilia | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Vibrio parahemolyticus | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Campylobacter | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Aspergillus niger | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
|
Test temperature=23°C
|
||||
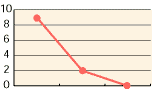
4. Spraying in space:
The airborne bacteria in space will be killed by sprayed hypochlorous acid.
The diagram below illustrates the counts of falling bacteria within one hour in a 6-bed ward in which hypochlorous acid (200ppm) was sprayed. The data was collected in the beginning and after 30 & 60 minutes with hypochlorous acid sprayed. During the test period, nurses moved in and out the ward as usual. The counts of falling bacteria were dropped dramatically in 30 minutes with hypochlorous acid sprayed and kept almost unchanged after the next 30 minutes. The status of MRSA, which was positive before spraying of hypochlorous acid, became negative after 30 minutes.
| Counts of falling bacteria | Changes in counts of falling bacteria |
|---|---|
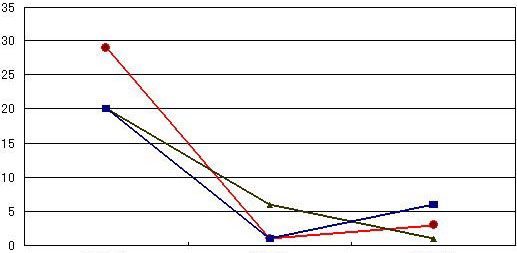 |
|
| Before spraying During spraying After spraying |
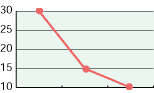
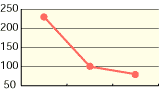
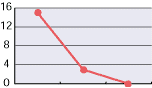
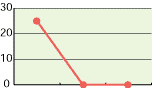
5. Hypochlorous acid for deodorization:
As shown in the diagrams below, hypochlorous acid is particularly effective in deodorizing organic matters. Moreover, it is necessary to deodorize the source of odors which come from bacteria mostly.
| CH3CHO | NH3 | H2S |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins |
| TMA | Methyl mercaptan | CH3COOH |
 |
 |
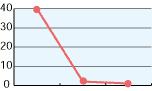 |
| 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins |
| Free effective chloride concentration in testing=80ppm | ||
In the past, the ordinary deodorant discharges aroma to restrain foul smells. Comparatively, hypochlorous acid transforms reek to odorless air through chemical reactions.
Particularly, ammonia, which is one of four major sources of foul smells, disappears as shown in chemical reactions below.
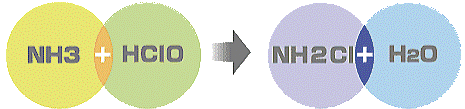 |
||||||
| Ammonia + hypochlorous acid |
|
|||||

※ Note: The technique of sterilization based on chloramine had been adopted by some nations in Europe and Japan in the 1920’s because chloramine chemically reacts with organic matters slowly and the residual effect restrains foul smells.
Hypochlorous acid stored in ultrasonic sprayers can be sprayed in consulting rooms, operating rooms or doghouses by animal hospitals for odor control. Furthermore, hypochlorous acid is very effective in deodorization of pets’ feces.
6. Safety of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid can be created in blood of a person in whom the invading bacteria or viruses are killed. That is, our bodies are very familiar with hypochlorous acid.
Test results for animal safety with hypochlorous acid (50ppm):
| Mistaken swallow | → | Normal |
|---|---|---|
| Acute toxicity test by the single oral medicine | ||
| Skin (eye) contact | No irritation | |
| Single skin irritation test; eye irritation test | ||
| Allergy | No allergy | |
| Allergy test | ||
| Cancer | No cancer induced | |
| Mutation test in convalescence (mutagenicity test) |
Application case of sterilizing water
5、Application case:
1. Cleaning of chopped vegetables

Super Aqua sterilizing water can be used in cleaning chopped vegetables. In this regard, chopped vegetables should contact well-agitated sterilizing water (for expanded contact surfaces because of bubbles) despite hypochlorous acid effectively sterilizing microbes within one minute. Conversely, the sterilization effect is worst when chopped vegetables are dipped in water for a long period. (During the long soak of vegetables, the sterilization is effective in the intermediate stage but the sterilizing water is transformed to clean water finally.)
Please add new Super Aqua sterilizing water and keep it running to maintain the sterilization effect.
2. Seafood and processed meat

There is no bacterium inside seafood or meat in the beginning. However, the meat may be contaminated by bacteria when the outer skin or viscera is removed during meat processing. To prevent food or meat in food contaminated by microbes, an operator should spray Super Aqua sterilizing water to clean meat while removing outer skin or viscera.
3. Sterilization and cleaning of beverage bottles and caps

The hygiene index will be increased when both beverage bottles in which drinking water is to be filled and surrounding bacteria are cleaned and sterilized by sterilizing water. Moreover, the effective high-quality cleaning process is constructed in a beverage production line because the beverage bottles are easily cleaned with low-concentration sterilizing water in a small space. Additionally, the second pollution is prevented indirectly with airborne bacteria removed by sterilizing water sprayed indoors.
CIP (Clean in Place)sterlization
Beverage plant or food factories with well CIP ( Clean in Place) sterlization is very important. Traditionally use boiler for making high temperature steam with certain pressure and temperature working the CIP sterlization for tanks/pipes and equipment before manufacturing or after manufactured so that ensure to kill Bacillus bacteria ( Included preparation took some 50 minutes). Replace with Super Aqua hypochlorous acid liquid would just take 5-10 minutes. (Bacillus bacteria can be well killed within 3 minutes)。If increase some higher temperature the process might be sorter possible.
Merits:
1. the sterilization time shorten significantly.
2. Reduce clients's fuel costs significantly (energy saving)
3. Increase capability of production, etc.
4. Sprayer-based sterilization in space

The sterilization can be done with two-fluid spraying and ultrasonic spraying.
The two-fluid spraying which relies on compressed air to atomize sterilizing water is available to a factory or a spacious site for removal of airborne bacteria and no contamination of falling bacteria.

It is recommended to use the ultrasonic sprayer in tranquil indoor spaces.
The hypochlorous acid sprayer is designed for a small-size space with the floor area less than 13 × 36 square feet or a business premise with the floor area of 75 × 36 square feet.
5. Hand washing and cleaning of utensils
A user can spray sterilizing water to sterilize and clean fingers, work boots, kitchenware (e.g., cutting board and knife), and utensils on equipment or floors.
It is important to keep sanitation of users’ work boots, utensils and surroundings in addition to hands.
6. Location and purpose
Locations and purposes to use SUPER AQUA sterilizing water:
| Location | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Food processing factory | Cleaning of food materials, utensils and workplaces |
| Seafood processing factory | Cleaning and defrosting of seafood; cleaning of utensils and workplaces |
| Beverage factory | Cleaning of bottles, utensils, machines, pipelines and indoor environment; indoor spraying |
| Kitchen | Cleaning of food materials, utensils and machines |
| Bakery | Cleaning of utensils and machines; indoor spraying |
| Stock farming | Spraying of environment |
| General manufacturer | Deodorization of wastes |
【Types and purposes of hypochlorous acid】
| Medical apparatus (topical bactericide) |
Food additive (Sterilizing material) |
Bleaching agent for sterilization and deodorization (grocery) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
For samples of hypochlorous-acid liquids, please contact us.
Except the applicant who had received samples several times, an ordinary applicant will receive Super Aqua hypochlorous acid liquid samples (200ppm; 25 liters) (freight collect).
Super Aqua will deliver samples to the applicant who completed the application accordingally. (NOTE: Some identified countries only )
Fanslly-800 Hypochlorous Acid Powder Series
Fanslly-800 Hypochlorous Acid Powder,
Easily Transform Water Become Hypochlorous Acid!!
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1 gram | 2 grams | 3.2 grams | 500 grams | 1000 grams |
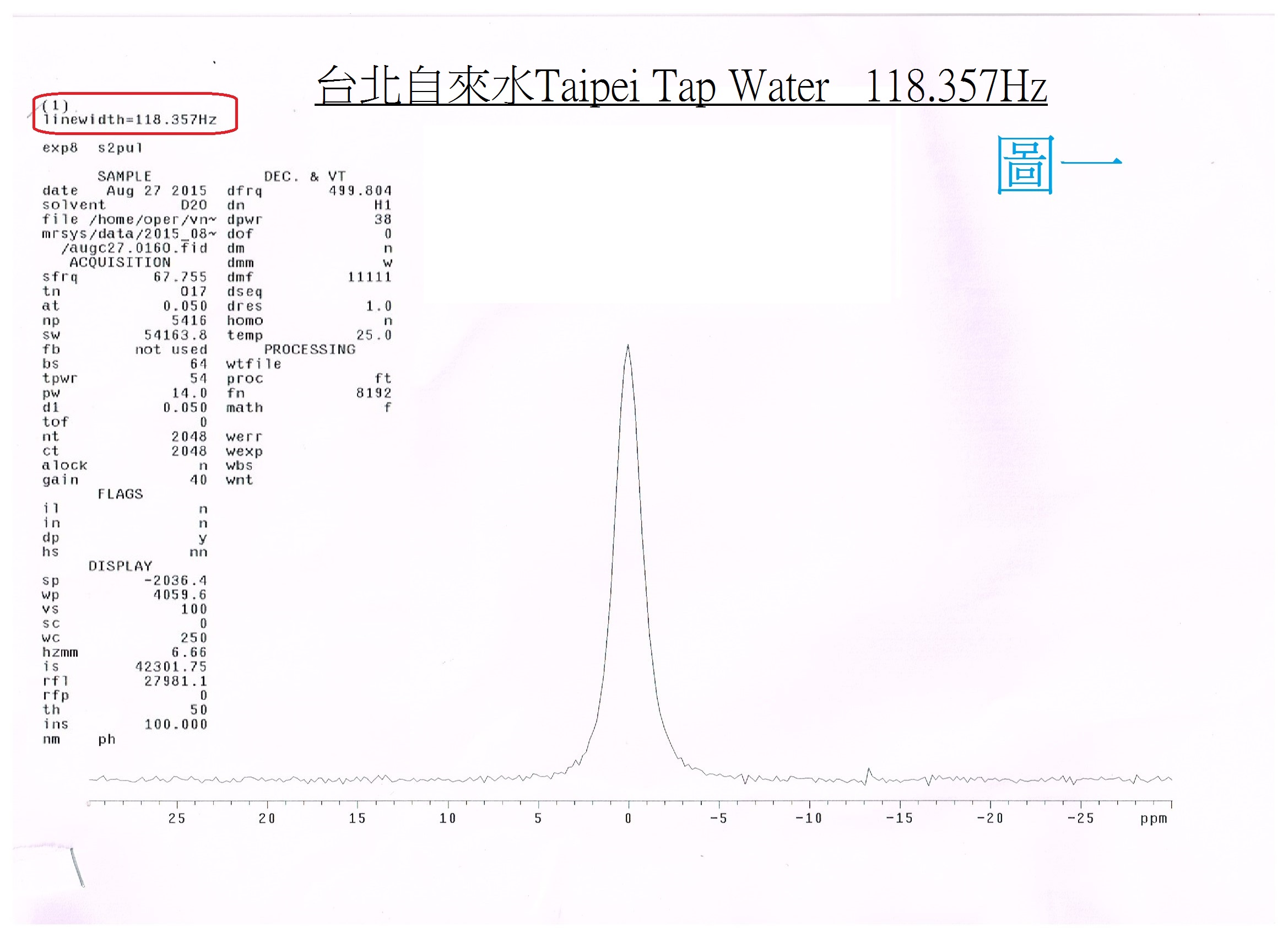
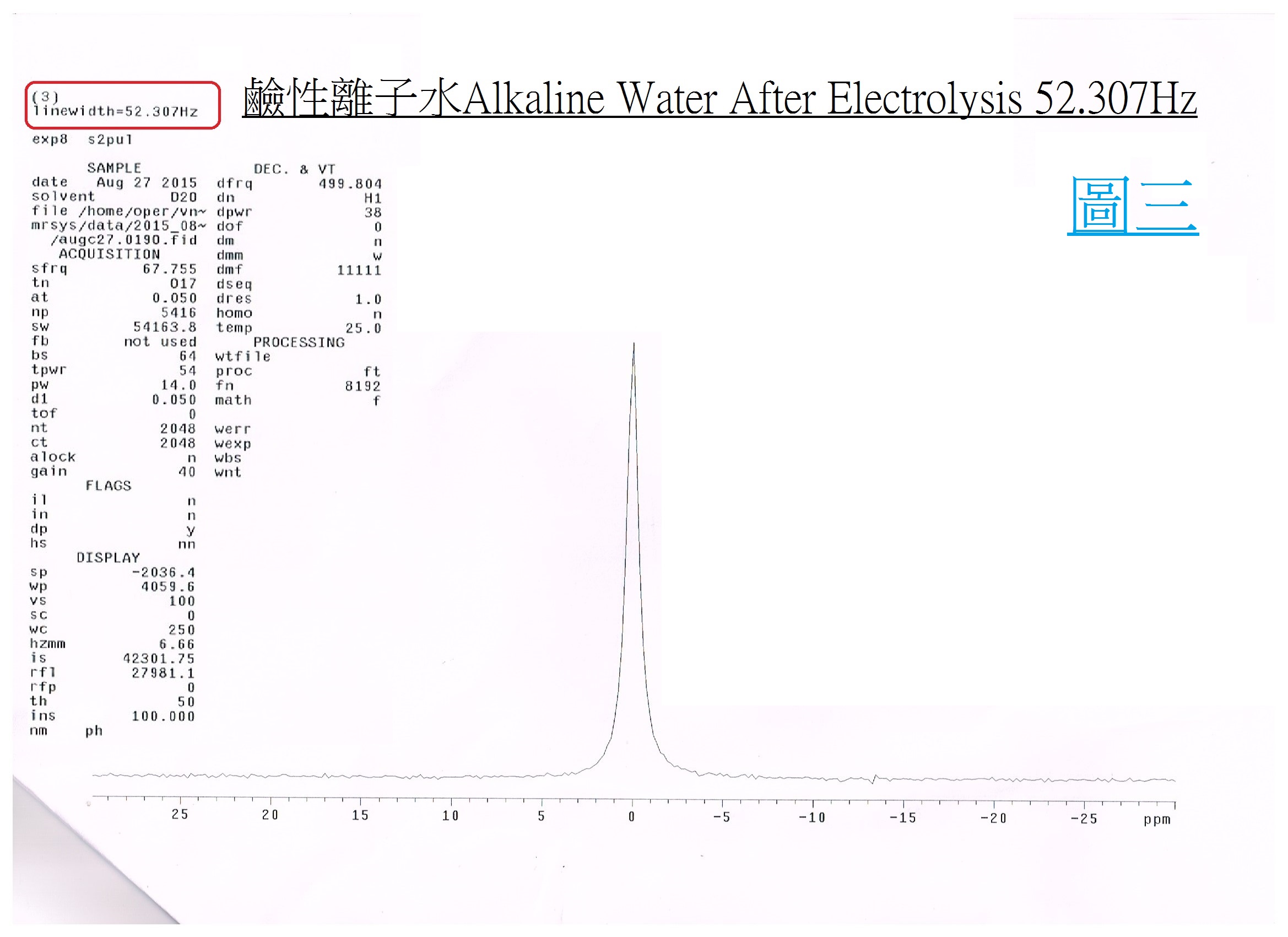
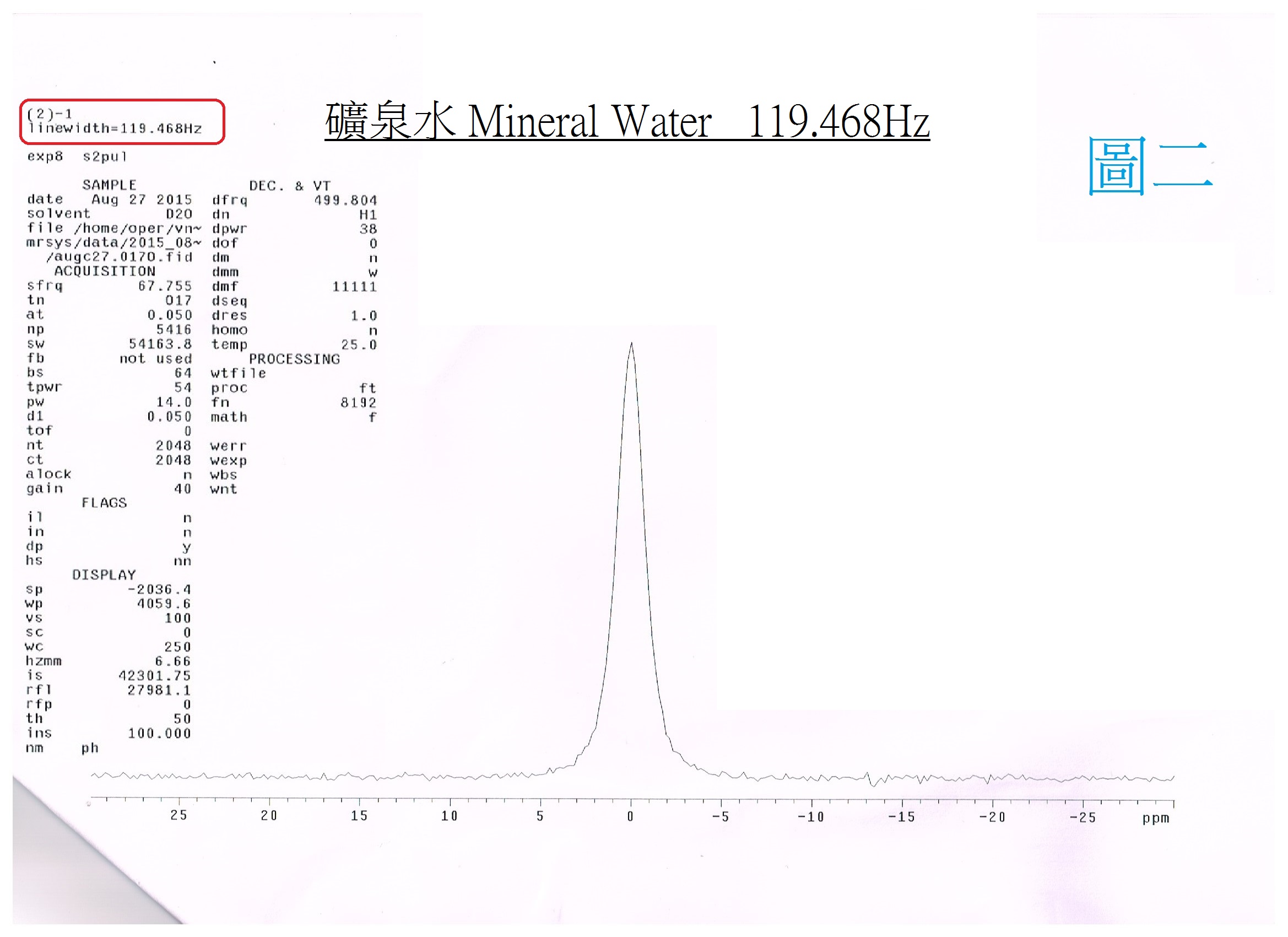
NMR Scientific Certification for Small-molecular Water Cluster
Small Cluster Water:Electrolyzed reduced water (alkaline ionized water) has been verified as small-molecular cluster water according to the NMR spectrometer. |
The alkaline ionized water is small cluster water, which can be measured by the NMR (Nuclear magnetic resonate spectrograph): the tap water is about 118Hz (PIC. 1); The mineral water is about 119Hz (PIC. 2); and the pH9 of alkaline ionized water (PIC. 3) is about 52Hz. |
|
During the electrolysis process, the water molecules will be recombined to small cluster water.
Easily absorbed by human body, the water with small cluster water is helpful for metabolism and can remove acidic substances and wastes from human body, therefore enhancing the inner environmental system, properly adjust the acidic physical condition and improve our health! |
Equipment for Alkaline Ionized Water
Technical features of Golden Alkalizer
Alkaline Ionized water: about 3,000L/hr
Acidic Ionized water: about 1,000L/hr
Comparisons of All Types of Bottled Drinking Water
|
Item Type |
Manufacturing process | pH value | Mineral | Water molecule cluster * Note 1 |
Water molecule (NMR) * Note 2 |
Taste (molecule cluster and hardness) |
Health Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline ionized water | (1) RO water + minerals→ electrolysis (2) natural water → electrolysis |
Alkaline (pH=9~9.5) |
Ionized minerals | 6 | Small (45Hz~55Hz) (depending on pH values) |
Palatable (Making tea or coffee, cocktail, cuisine, etc.) |
Small-molecule water active hydrogen (hydrogen) hydrogy ion Ca(OH)2 ionized minerals |
| Natural mineral water natural water |
Mountain spring groundwater |
Weak alkaline or acid (pH≒7.5) |
Natural minerals; natural minerals with trace elements |
8~12 (depending on locations and water conditions) |
94Hz (depending on locations; 80Hz (Village of Long Life)) |
Tastes depending on hardness and water molecule clusters are different from one another. | Natural minerals; trace elements |
| Mineralized drinking water | Tap water → RO water + artificial mineral | Acid (pH≒6.5) |
Pure water with artificial minerals added | 8~10 | 88Hz~90Hz in general (RO water) |
Palatable | Small-molecule water minerals |
| Pure water distilled water |
Groundwater or tap water → RO water or distillation processing |
Acid (pH≒6.0) neutral or acidic (distilled water) |
Nil | 8~10 13~15 |
Pure water: 88-90Hz; distilled water: 140Hz |
Good taste for pure water (no hardness); taste worsen for distilled water with larger molecule clusters |
It is not healthy to drink pure (distilled) water for a long period. * Note 3: The small-molecule water with little mineral is not healthy. |
|
* Note 1: Data of Kazuhiro Matsushita, JEOL |
 English
English  繁體中文
繁體中文  简体中文
简体中文